Topological data scripting: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == |
== Introduction == |
||
First to use the Part module functionality you have to load the Part module into the |
First to use the Part module functionality you have to load the Part module into the interpreter: |
||
<code python> |
<code python> |
||
import Part |
import Part |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
=== Class Diagram === |
=== Class Diagram === |
||
This is |
This is a UML overview about the most important classes of the Part module: |
||
[[Image:Part_Classes.jpg|center|Python classes of the Part module]] |
[[Image:Part_Classes.jpg|center|Python classes of the Part module]] |
||
=== Geometry === |
=== Geometry === |
||
The |
The geomtric objects are the building block of all topological objects: |
||
* '''Geom''' Base class of the geometric objects |
* '''Geom''' Base class of the geometric objects |
||
* '''Line''' A straight line in 3D, defined by starting point and and point |
* '''Line''' A straight line in 3D, defined by starting point and and point |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
* '''SHAPE''' A generic term covering all of the above. |
* '''SHAPE''' A generic term covering all of the above. |
||
== Creating |
== Creating basic types == |
||
You can directly create basic topological objects through the module: |
You can directly create basic topological objects through the module: |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
[[Image:Wire.png|right|Wire]] |
[[Image:Wire.png|right|Wire]] |
||
We will now create a topology by constructing it out of simpler geometry. |
We will now create a topology by constructing it out of simpler geometry. |
||
As a case study we use a |
As a case study we use a part as seen in the picture which consists of |
||
four |
four vertexes, two circles and two lines. |
||
=== Creating Geometry === |
=== Creating Geometry === |
||
First we have to create the distinct geometric parts of this |
First we have to create the distinct geometric parts of this wire. |
||
And we have to take care that the |
And we have to take care that the vertexes of the geometric parts |
||
are at the '''same''' position. Otherwise we can later on not |
are at the '''same''' position. Otherwise we can later on not |
||
connect the geometric parts to a topology! |
|||
So we create first the points: |
So we create first the points: |
||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
==== Arc ==== |
==== Arc ==== |
||
[[Image:Circel.png|right|Circle]] |
[[Image:Circel.png|right|Circle]] |
||
To create |
To create an arc of circle we make a helper point and create the arc of circle |
||
through three points: |
through three points: |
||
<code python> |
<code python> |
||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
==== Line ==== |
==== Line ==== |
||
[[Image:Line.png|right|Line]] |
[[Image:Line.png|right|Line]] |
||
The |
The line can be created very simple out of the points: |
||
<code python> |
<code python> |
||
L1 = Part.Line(V1,V2) |
L1 = Part.Line(V1,V2) |
||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
==== Make a prism ==== |
==== Make a prism ==== |
||
Now extrude the wire in a direction and make |
Now extrude the wire in a direction and make an actual 3D shape: |
||
<code python> |
<code python> |
||
P = S1.makePrism(Base.Vector(0,0,10)) |
P = S1.makePrism(Base.Vector(0,0,10)) |
||
Revision as of 15:13, 10 July 2008
Introduction
First to use the Part module functionality you have to load the Part module into the interpreter:
import Part
Class Diagram
This is a UML overview about the most important classes of the Part module:

Geometry
The geomtric objects are the building block of all topological objects:
- Geom Base class of the geometric objects
- Line A straight line in 3D, defined by starting point and and point
- Circle Circle or circle segment defined by a center point and start and end point
- ...... And soon some more ;-)
Topology
The following topological data types are available:
- COMPOUND A group of any type of topological object.
- COMPSOLID A composite solid is a set of solids connected by their faces. It expands the notions of WIRE and SHELL to solids.
- SOLID A part of space limited by shells. It is three dimensional.
- SHELL A set of faces connected by their edges. A shell can be open or closed.
- FACE In 2D it is part of a plane; in 3D it is part of a surface. Its geometry is constrained (trimmed) by contours. It is two dimensional.
- WIRE A set of edges connected by their vertices. It can be an open or closed contour depending on whether the edges are linked or not.
- EDGE A topological element corresponding to a restrained curve. An edge is generally limited by vertices. It has one dimension.
- VERTEX A topological element corresponding to a point. It has zero dimension.
- SHAPE A generic term covering all of the above.
Creating basic types
You can directly create basic topological objects through the module:
b = Part.createBox(0,0,0,100,100,100)
Part.show(b)
Exploring shapes
You can explore the topological data structure:
b = Part.createBox(0,0,0,100,100,100)
b.Wires
w = b.Wires[0]
w
w.Wires
w.Vertexes
Part.show(w)
w.Edges
e = w.Edges[0]
e.Vertexes
v = e.Vertexes[0]
v.Point
Creating Topology

We will now create a topology by constructing it out of simpler geometry. As a case study we use a part as seen in the picture which consists of four vertexes, two circles and two lines.
Creating Geometry
First we have to create the distinct geometric parts of this wire. And we have to take care that the vertexes of the geometric parts are at the same position. Otherwise we can later on not connect the geometric parts to a topology!
So we create first the points:
from FreeCAD import Base
V1 = Base.Vector(0,10,0)
V2 = Base.Vector(30,10,0)
V3 = Base.Vector(30,-10,0)
V4 = Base.Vector(0,-10,0)
Arc

To create an arc of circle we make a helper point and create the arc of circle
through three points:
VC1 = Base.Vector(-10,0,0)
C1 = Part.Arc(V1,VC1,V4)
- and the second one
VC2 = Base.Vector(40,0,0)
C2 = Part.Arc(V2,VC2,V3)
Line
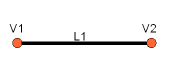
The line can be created very simple out of the points:
L1 = Part.Line(V1,V2)
- and the second one
L2 = Part.Line(V4,V3)
Put all together
The last step is to put the geometric base elements together
and bake a topological shape:
S1 = Part.Shape([C1,C2,L1,L2])
Make a prism
Now extrude the wire in a direction and make an actual 3D shape:
P = S1.makePrism(Base.Vector(0,0,10))