Sketcher Workbench: Difference between revisions
(Added link to Sketcher_CompConstrainRadDia.) |
(Removed references to V0.20.) |
||
| (251 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
|IconR=Workbench_Spreadsheet.svg |
|IconR=Workbench_Spreadsheet.svg |
||
}} |
}} |
||
<!--T:197--> |
|||
{{VeryImportantMessage|This page has been marked for translation. But it is still a work in progress!!!}} |
|||
<!--T:123--> |
<!--T:123--> |
||
| Line 20: | Line 23: | ||
<!--T:2--> |
<!--T:2--> |
||
With the FreeCAD [[Image:Workbench_Sketcher.svg|24px]] [[Sketcher_Workbench|Sketcher Workbench]] 2D sketches intended for use in other workbenches can be created. 2D sketches are the starting point for many CAD models. They typically define the profiles and paths for operations to create 3D shapes. A model may depend on several sketches for its final shape. |
|||
The FreeCAD [[Image:Workbench_Sketcher.svg|24px]] [[Sketcher_Workbench|Sketcher Workbench]] is used to create 2D geometries intended for use in the [[Image:Workbench_PartDesign.svg|24px]] [[PartDesign_Workbench|PartDesign Workbench]], [[Image:Workbench_Arch.svg|24px]] [[Arch_Workbench|Arch Workbench]], and other workbenches. Generally, a 2D drawing is considered the starting point for most CAD models, as a 2D sketch can be "extruded" to create a 3D shape; further 2D sketches can be used to create other features like pockets, ridges, or extrusions on top of the previously built 3D shapes. Together with boolean operations defined in the [[Image:Workbench_Part.svg|24px]] [[Part Workbench|Part Workbench]], the Sketcher forms the basis of the [[constructive solid geometry|constructive solid geometry]] (CSG) method of building solids. Moreover, together with the [[Image:Workbench_PartDesign.svg|24px]] [[PartDesign_Workbench|PartDesign Workbench]] operations, the Sketcher also forms the basis of the [[feature editing|feature editing]] methodology of creating solids. |
|||
<!--T:198--> |
|||
Together with boolean operations defined in the [[Image:Workbench_Part.svg|16px]] [[Part Workbench|Part Workbench]], the Sketcher Workbench, or "The Sketcher" for short, forms the basis of the [[constructive solid geometry|constructive solid geometry]] (CSG) method of building solids. Together with [[Image:Workbench_PartDesign.svg|16px]] [[PartDesign_Workbench|PartDesign Workbench]] operations, it also forms the basis of the [[feature editing|feature editing]] methodology of creating solids. But many other workbenches use sketches as well. |
|||
<!--T:3--> |
<!--T:3--> |
||
The Sketcher workbench features |
The Sketcher workbench features [[#Constraints|constraints]], allowing 2D shapes to follow precise geometrical definitions in terms of length, angles, and relationships (horizontality, verticality, perpendicularity, etc.). A constraint solver calculates the constrained-extent of 2D geometry and allows interactive exploration of the degrees-of-freedom of the sketch. |
||
<!--T:11--> |
|||
The Sketcher is not intended for producing 2D blueprints. Once sketches are used to generate a solid feature, they are automatically hidden and Constraints are only visible in Sketch edit mode. If you only need to produce 2D views for print, and don't want to create 3D models, check out the [[Draft_Workbench|Draft workbench]]. |
|||
</translate> |
</translate> |
||
| Line 31: | Line 40: | ||
{{Caption|A fully constrained sketch}} |
{{Caption|A fully constrained sketch}} |
||
== |
== Constraints == <!--T:199--> |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:7--> |
||
Constraints are used to limit the degrees of freedom of an object. For example, a line without constraints has 4 Degrees Of Freedom (abbreviated as "DoF"): it can be moved horizontally or vertically, it can be stretched, and it can be rotated. |
|||
To explain how the Sketcher works, it may be useful to compare it to the "traditional" way of drafting. |
|||
<!--T:8--> |
|||
Applying a horizontal or vertical constraint, or an angle constraint (relative to another line or to one of the axes), will limit its capacity to rotate, thus leaving it with 3 degrees of freedom. Locking one of its points in relation to the origin will remove another 2 degrees of freedom. And applying a dimension constraint will remove the last degree of freedom. The line is then considered '''fully-constrained'''. |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:9--> |
||
Objects can be constrained in relation to one another. Two lines can be joined through one of their points with the coincident point constraint. An angle can be set between them, or they can be set perpendicular. A line can be tangent to an arc or a circle, and so on. A complex Sketch with multiple objects may have a number of different solutions, and making it '''fully-constrained''' can mean that just one of these possible solutions has been reached based on the applied constraints. |
|||
The traditional way of CAD drafting inherits from the old [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drawing_board drawing board]. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiview_orthographic_projection Orthogonal (2D) views] are drawn manually and intended for producing technical drawings (also known as blueprints). Objects are drawn precisely to the intended size or dimension. If you want to draw an horizontal line 100mm in length starting at (0,0), you activate the line tool, either click on the screen or input the (0,0) coordinates for the first point, then make a second click or input the second point coordinates at (100,0). Or you will draw your line without regard to its position, and move it afterwards. When you've finished drawing your geometries, you add dimensions to them. |
|||
<!--T:10--> |
|||
There are two kinds of constraints: geometric and dimensional. They are detailed in the [[#Tools|Tools]] section below. |
|||
=== Driving vs. reference constraints === <!--T:200--> |
|||
<!--T:6--> |
|||
The '''Sketcher''' moves away from this logic. Objects do not need to be drawn exactly as you intend to, because they will be defined later on by constraints. Objects can be drawn loosely, and as long as they are unconstrained, can be modified. They are in effect "floating" and can be moved, stretched, rotated, scaled, and so on. This gives great flexibility in the design process. |
|||
=== Edit constraints === <!--T:201--> |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:202--> |
||
When a [[Sketcher_ToggleDrivingConstraint|driving constraint]] is created, and if the {{MenuCommand|Ask for value after creating a dimensional constraint}} [[Sketcher_Preferences#Display|preference]] is selected (default), a dialog opens to edit its value. |
|||
Instead of dimensions, Constraints are used to limit the degrees of freedom of an object. For example, a line without constraints has 4 Degrees Of Freedom (abbreviated as "DOF"): it can be moved horizontally or vertically, it can be stretched, and it can be rotated. |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:203--> |
||
[[Image:Sketcher_Edit_Constraint.png|Sketcher_Edit_Constraint.png]] |
|||
Applying a horizontal or vertical constraint, or an angle constraint (relative to another line or to one of the axes), will limit its capacity to rotate, thus leaving it with 3 degrees of freedom. Locking one of its points in relation to the origin will remove another 2 degrees of freedom. And applying a dimension constraint will remove the last degree of freedom. The line is then considered '''fully-constrained'''. |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:204--> |
||
You can enter a numerical value or an [[Expressions|expression]], and it is possible to name the constraint to facilitate its use in other expressions. You can also check the {{MenuCommand|Reference}} checkbox to switch the constrain to reference mode. |
|||
Multiple objects can be constrained between one another. Two lines can be joined through one of their points with the coincident point constraint. An angle can be set between them, or they can be set perpendicular. A line can be tangent to an arc or a circle, and so on. A complex Sketch with multiple objects will have a number of different solutions, and making it '''fully-constrained''' means that just one of these possible solutions has been reached based on the applied constraints. |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:205--> |
||
To edit the value of an existing dimensional constraint do one of the following: |
|||
* Double-click the constraint value in the [[3D_view|3D view]]. |
|||
* Double-click the constraint in the [[Sketcher_Dialog|Sketcher Dialog]]. |
|||
* Right-click the constraint in the Sketcher Dialog and select the {{MenuCommand|Change value}} option from the context menu. |
|||
=== Reposition constraints === <!--T:206--> |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:207--> |
||
Constraints can be repositioned in the 3D view by dragging. Hold down the left mouse button over the constraint value and move the mouse. |
|||
The Sketcher is not intended for producing 2D blueprints. Once sketches are used to generate a solid feature, they are automatically hidden. Constraints are only visible in Sketch edit mode. |
|||
<!--T: |
== Profile sketches == <!--T:208--> |
||
If you only need to produce 2D views for print, and don't want to create 3D models, check out the [[Draft_Workbench|Draft workbench]]. Unlike Sketcher elements, Draft objects don't use constraints; they are simple shapes defined at the moment of creation. Both Draft and Sketcher can be used for 2D geometry drawing, and 3D solid creation, although their preferred use is different; the Sketcher is normally used together with [[Part Workbench|Part]] and [[PartDesign Workbench|PartDesign]] to create solids; Draft is normally used for simple planar drawings over a grid, as when drawing an architectural floor plan; in these situations Draft is mostly used together with the [[Arch Workbench|Arch Workbench]]. The tool [[Draft Draft2Sketch|Draft2Sketch]] converts a Draft object to a Sketch object, and vice versa; many tools that require a 2D element as input work with either type of object as an internal conversion is done automatically. |
|||
<!--T:209--> |
|||
To create a sketch that can be used as a profile for generating solids certain rules must be followed: |
|||
* The sketch must contain only closed contours. Gaps between endpoints, however small, are not allowed. |
|||
* Contours can be nested, to create voids, but should not self-intersect or intersect other contours. |
|||
* Contours cannot share edges with other contours. Duplicate edges should be avoided. |
|||
* T-connections, that is more than two edges sharing a common point, or a point touching an edge, are not allowed. |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:210--> |
||
These rules do not apply to construction geometry (default color blue), which is not shown outside edit mode, or if the sketch is used for a different purpose. Depending on the workbench and the tool that will use the profile sketch, additional restrictions may apply. |
|||
A Sketch is always 2-dimensional (2D). To create a solid, a 2D Sketch of a single enclosed area is created and then either Padded or Revolved to add the 3rd dimension, creating a 3D solid from the 2D Sketch. |
|||
<!--T: |
== Drawing aids == <!--T:211--> |
||
If a Sketch has segments that cross one another, places where a Point is not directly on a segment, or places where there are gaps between endpoints of adjacent segments, Pad or Revolve won't create a solid. Sometimes a Sketch which contains lines which cross one another will work for a simple operation such as Pad, but later operations such as Linear Pattern will fail. It is best to avoid crossing lines. The exception to this rule is that it doesn't apply to Construction (blue) Geometry. |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:212--> |
||
The Sketcher Workbench has several drawing aids and other features that can help when creating geometry and applying constraints. |
|||
Inside the enclosed area we can have smaller non-overlapping areas. These will become voids when the 3D solid is created. |
|||
<!--T: |
=== Continue modes === <!--T:213--> |
||
Once a Sketch is fully constrained, the Sketch features will turn green; Construction Geometry will remain blue. It is usually "finished" at this point and suitable for use in creating a 3D solid. However, once the Sketch dialog is closed it may be worthwhile going to [[Image:Workbench_Part.svg|24px]] [[Part_Workbench|Part Workbench]] and running {{Button|[[File:Part_CheckGeometry.svg|16px]] [[Part_CheckGeometry|Check geometry]]}} to ensure there are no features in the Sketch which may cause later problems. |
|||
<!--T:214--> |
|||
There are two continue modes: '''Geometry creation "Continue Mode"''' and '''Constraint creation "Continue Mode"'''. If these are checked (default) in the [[Sketcher_Preferences#Display|preferences]], related tools will restart after finishing. To exit an continuous tool press {{KEY|Esc}} or the right mouse button. This must be repeated if a continuous geometry tool has already received input. You can also exit a continuous tool by starting another geometry or constraint creation tool. Note that pressing {{KEY|Esc}} if no tool is active will exit sketch edit mode. Uncheck the '''Esc can leave sketch edit mode''' [[Sketcher_Preferences#General|preference]] if you often inadvertently press {{KEY|Esc}} too many times. |
|||
=== Auto constraints === <!--T:215--> |
|||
<!--T:216--> |
|||
In sketches that have '''Auto constraints''' checked (default) several constraints are applied automatically when hovering the cursor properly (their symbols are displayed next to the cursor before applying). This is a per-sketch setting that can be changed in the [[Sketcher_Dialog#Constraints|Sketcher Dialog]] or by changing the {{PropertyView|Autoconstraints}} [[Property_editor|property]] of the sketch. The following constraints are applied automatically: |
|||
* [[Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident|Coincident]] |
|||
* [[Sketcher_ConstrainPointOnObject|Point on object]] |
|||
* [[Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal|Horizontal]] |
|||
* [[Sketcher_ConstrainVertical|Vertical]] |
|||
* [[Sketcher_ConstrainTangent|Tangent]] |
|||
* {{Version|0.22}}: [[Sketcher_ConstrainSymmetric|Symmetric]] (line midpoint) |
|||
=== Snapping === <!--T:217--> |
|||
<!--T:218--> |
|||
{{Version|0.21}} |
|||
<!--T:219--> |
|||
It is possible to [[Sketcher_Snap|snap]] to grid lines and grid intersection, to edges of geometry and midpoints of lines and arcs, and to certain angles. Please note that snapping does not produce constraints in and of itself. For example, only if Auto constraints is switched on will snapping to an edge produce a [[Sketcher_ConstrainPointOnObject|Point on object constraint]]. But just picking a point on the edge would then have the same result. |
|||
=== On-View-Parameters === <!--T:220--> |
|||
<!--T:221--> |
|||
{{Version|0.22}} |
|||
<!--T:222--> |
|||
Depending on the selected option in the [[Sketcher_Preferences#General|preferences]] only the dimensional On-View-Parameters or both the dimensional and the positional On-View-Parameters can be enabled. Positional parameters allow the input of exact coordinates, for example the center of a circle, or the start point of a line. Dimensional parameters allow the input of exact dimensions, for example the radius of a circle, or the length and angle of a line. On-View-Parameters are not available for all tools. |
|||
</translate> |
|||
[[Image:Sketcher_On_view_parameters_positional.png]] |
|||
<translate> |
|||
<!--T:223--> |
|||
{{Caption|Determining the center point of a circle with the positional parameters enabled}} |
|||
</translate> |
|||
[[Image:Sketcher_On_view_parameters_dimensional.png]] |
|||
<translate> |
|||
<!--T:224--> |
|||
{{Caption|Determining the radius of a circle with the dimensional parameters enabled}} |
|||
<!--T:225--> |
|||
If values are entered and confirmed by pressing {{KEY|Enter}} or {{KEY|Tab}}, related constraints are added automatically. If two parameters are displayed at the same time, for example the X and Y coordinate of a point, it is possible to enter one value and pick a point to define the other. Depending on the object additional constraints may be required to fully constrain it. Constraints resulting from On-View-Parameters take precedence over those that may result from [[Sketcher_Dialog#Constraints|Auto constraints]]. |
|||
</translate> |
|||
[[Image:Sketcher_ArcExample3.png|300px]] |
|||
<translate> |
|||
<!--T:226--> |
|||
{{Caption|Arc created by entering all On-View-Parameters with resulting automatically created constraints}} |
|||
=== Coordinate display === <!--T:227--> |
|||
<!--T:228--> |
|||
If the '''Show coordinates beside cursor while editing''' [[Sketcher_Preferences#Display|preference]] is checked (default), the parameters of the current geometry tool (coordinates, radius, or length and angle) are displayed next to the cursor. This is deactivated while On-View-Parameters are shown. |
|||
== Selection == <!--T:229--> |
|||
<!--T:230--> |
|||
No need for Ctrl, but... |
|||
Select in Sketcher Dialog... |
|||
=== Box selection === <!--T:231--> |
|||
=== Connected geometry selection === <!--T:232--> |
|||
== Copy, cut and paste == <!--T:233--> |
|||
<!--T:234--> |
|||
{{Version|0.22}} |
|||
<!--T:235--> |
|||
The standard keyboard shortcuts can be used to copy, {{KEY|Ctrl}}+{{KEY|C}}, cut, {{KEY|Ctrl}}+{{KEY|X}}, and paste, {{KEY|Ctrl}}+{{KEY|V}}, the currently selected Sketcher geometry including related constraints. But these tools are also available from the {{MenuCommand|Sketch → Sketcher tools}} menu. They can be used within the same sketch but also between different sketches or separate instances of FreeCAD. Since the data is copied to the clipboard in the form of Python code, it can be used in other ways too (e.g. shared on the forum). |
|||
== Tools == <!--T:144--> |
== Tools == <!--T:144--> |
||
<!--T:16--> |
<!--T:16--> |
||
The Sketcher Workbench tools are |
The Sketcher Workbench tools are located in the Sketch menu and/or several toolbars. {{Version|0.21}}: Almost all Sketcher toolbars are only displayed while a sketch is in edit mode. The only exception is the [[#Sketcher_toolbar|Sketcher toolbar]] which is only displayed if no sketch is in edit mode. |
||
<!--T:177--> |
|||
{{Version|0.21}}: If a sketch is in edit mode the Structure toolbar is hidden as none of its tools can then be used. |
|||
=== General === <!--T:126--> |
=== General === <!--T:126--> |
||
==== Sketcher toolbar ==== <!--T:164--> |
|||
<!--T:23--> |
<!--T:23--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_NewSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_NewSketch|Create sketch]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_NewSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_NewSketch|Create sketch]]: Creates a new sketch and opens the [[Sketcher_Dialog|Sketcher Dialog]] to edit it. |
||
<!--T:24--> |
<!--T:24--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_EditSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_EditSketch|Edit sketch]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_EditSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_EditSketch|Edit sketch]]: Opens the Sketcher Dialog to edit an existing sketch. |
||
<!--T:28--> |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_MapSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_MapSketch|Attach sketch]]: Attaches a sketch to selected geometry. |
|||
<!--T:29--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_ReorientSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ReorientSketch|Reorient sketch]]: Places a sketch on one of the main planes with an optional offset. It can also be used to detach a sketch. |
|||
<!--T:30--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_ValidateSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ValidateSketch|Validate sketch]]: Can analyze and repair a sketch that is no longer editable or has invalid constraints, or add missing coincident constraints. |
|||
<!--T:31--> |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_MergeSketches.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_MergeSketches|Merge sketches]]: Merges two or more sketches. |
|||
<!--T:32--> |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_MirrorSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_MirrorSketch|Mirror sketch]]: Mirrors sketches along their X axis, Y axis, or origin. |
|||
==== Sketcher Edit Mode toolbar ==== <!--T:165--> |
|||
<!--T:25--> |
<!--T:25--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_LeaveSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_LeaveSketch|Leave sketch]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_LeaveSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_LeaveSketch|Leave sketch]]: Finishes sketch edit mode and closes the [[Sketcher_Dialog|Sketcher Dialog]]. |
||
<!--T:26--> |
<!--T:26--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_ViewSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ViewSketch|View sketch]]: Sets the |
* [[Image:Sketcher_ViewSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ViewSketch|View sketch]]: Sets the [[3D_view|3D view]] perpendicular to the sketch plane. |
||
<!--T:27--> |
<!--T:27--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_ViewSection.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ViewSection|View section]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_ViewSection.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ViewSection|View section]]: Toggles a temporary section plane that hides any objects and parts of objects in front of the sketch plane. |
||
==== Sketcher edit tools toolbar ==== <!--T:175--> |
|||
<!--T:28--> |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_MapSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_MapSketch|Map sketch to face]]: Maps a sketch to the previously selected face of a solid. |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:166--> |
||
* [[ |
* [[Image:Sketcher_Grid.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Grid|Toggle grid]]: Toggles the grid in the sketch currently being edited. Settings can be changed in the related menu. {{Version|0.21}} |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:167--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_Snap.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Snap|Toggle snap]]: Toggles snapping in all sketches. Settings can be changed in the related menu. {{Version|0.21}} |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_ValidateSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ValidateSketch|Validate sketch]]: Verify the tolerance of different points and adjust them. |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:176--> |
||
* [[Image: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_RenderingOrder.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_RenderingOrder|Configure rendering order]]: The rendering order of all sketches can be changed in the related menu. {{Version|0.21}} |
||
<!--T: |
==== Other ==== <!--T:168--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_MirrorSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_MirrorSketch|Mirror sketch]]: Mirror a sketch along the x-axis, the y-axis or the origin. |
|||
<!--T:127--> |
<!--T:127--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_StopOperation.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_StopOperation|Stop operation]]: |
* [[File:Sketcher_StopOperation.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_StopOperation|Stop operation]]: Stops any currently running geometry or constraint creation tool. |
||
===Sketcher geometries=== <!--T:33--> |
===Sketcher geometries=== <!--T:33--> |
||
| Line 128: | Line 237: | ||
<!--T:35--> |
<!--T:35--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CreatePoint.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreatePoint|Point]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_CreatePoint.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreatePoint|Point]]: Creates a point. |
||
<!--T:36--> |
<!--T:36--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateLine.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateLine|Line]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateLine.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateLine|Line]]: Creates a line. {{Version|0.22}}: The tool has three modes. |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:180--> |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCreateArc">[[Image:Sketcher_CreateArc.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Create arc:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCreateArc pages redirect here--> |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CompCreateArc.png|48px]] [[Sketcher_CompCreateArc|Create an arc]]: This is an icon menu in the Sketcher toolbar that holds the following commands: |
|||
<!--T:37--> |
<!--T:37--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateArc.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateArc|Arc]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateArc.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateArc|Arc by center]]: Creates an arc by its center and its endpoints. {{Version|0.22}}: Or by its endpoints and a point along the arc. |
||
<!--T:38--> |
<!--T:38--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_Create3PointArc.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Create3PointArc|Arc by 3 points]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_Create3PointArc.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Create3PointArc|Arc by 3 points]]: Creates an arc by its endpoints and a point along the arc. {{Version|0.22}}: This is the same tool as [[Sketcher_CreateArc|Arc by center]] but with a different initial mode. |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:181--> |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCreateCircle">[[Image:Sketcher_CreateCircle.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Create circle:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCreateCircle pages redirect here--> |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CompCreateCircle.png|48px]] [[Sketcher_CompCreateCircle|Create a circle]]: This is an icon menu in the Sketcher toolbar that holds the following commands: |
|||
<!--T:39--> |
<!--T:39--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateCircle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateCircle|Circle]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateCircle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateCircle|Circle by center]]: Creates a circle by its center and a point along the circle. {{Version|0.22}}: Or by three points along the circle. |
||
<!--T:40--> |
<!--T:40--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_Create3PointCircle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Create3PointCircle|Circle by 3 points]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_Create3PointCircle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Create3PointCircle|Circle by 3 points]]: Creates a circle by three points along the circle. {{Version|0.22}}: This is the same tool as [[Sketcher_CreateCircle|Circle by center]] but with a different initial mode. |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:182--> |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCreateConic">[[Image:Sketcher_Conics.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Create conic:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCreateConic pages redirect here--> |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CompCreateConic.png|48px]] [[Sketcher_CompCreateConic|Create a conic]]: The sketcher provides the following conical sections. Unlike B-splines they can be used with all sorts of constraints such as [[Sketcher ConstrainTangent|Tangent]], [[Sketcher ConstrainPointOnObject|Point On Object]], or [[Sketcher ConstrainPerpendicular|Perpendicular]]. |
|||
: Ellipses, hyperbolas and parabolas are called "conics" because they are types of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conic_section conic sections]. |
|||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateEllipseByCenter.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateEllipseByCenter|Ellipse by center]]: Draws an ellipse by center point, major radius point and minor radius point. |
|||
<!--T:150--> |
|||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateEllipseBy3Points.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateEllipseBy3Points|Ellipse by 3 points]]: Draws an ellipse by major diameter (2 points) and minor radius point. |
|||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateEllipseByCenter.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateEllipseByCenter|Ellipse by center]]: Creates an ellipse by its center, an endpoint of one of its axes, and a point along the ellipse. {{Version|0.22}}: Or by both endpoints of one of its axes and a point along the ellipse. |
|||
<!--T:151--> |
|||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateArcOfEllipse.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateArcOfEllipse|Arc of ellipse]]: Draws an arc of ellipse by center point, major radius point, starting point and ending point. |
|||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateEllipseBy3Points.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateEllipseBy3Points|Ellipse by 3 points]]: Creates an ellipse by the endpoints of one of its axes and a point along the ellipse. {{Version|0.22}}: This is the same tool as [[Sketcher_CreateEllipseByCenter|Ellipse by center]] but with a different initial mode. |
|||
<!--T:152--> |
|||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateArcOfHyperbola.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateArcOfHyperbola|Arc of hyperbola]]: Draws an arc of hyperbola. |
|||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateArcOfEllipse.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateArcOfEllipse|Arc of ellipse]]: Creates an arc of ellipse. |
|||
<!--T:153--> |
|||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateArcOfParabola.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateArcOfParabola|Arc of parabola]]: Draws an arc of parabola. |
|||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateArcOfHyperbola.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateArcOfHyperbola|Arc of hyperbola]]: Creates an arc of hyperbola. |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:154--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateArcOfParabola.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateArcOfParabola|Arc of parabola]]: Creates an arc of parabola. |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CompCreateBSpline.png|48px]] [[Sketcher_CompCreateBSpline|Create a B-spline]]: This is an icon menu in the Sketcher toolbar that holds the following commands: |
|||
<!--T:183--> |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_CreateBSpline.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateBSpline|B-spline]]: Draws a B-spline curve by its control points. |
|||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCreateBSpline">[[Image:Sketcher_CreateBSpline.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] B-spline:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCreateBSpline pages redirect here--> |
|||
<!--T:155--> |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_CreatePeriodicBSpline.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreatePeriodicBSpline|Periodic B-spline]]: Draws a periodic (closed) B-spline curve by its control points. |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_CreateBSpline.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateBSpline|B-spline by control points]]: Creates a B-spline curve from control points. |
|||
<!--T:156--> |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_CreatePeriodicBSpline.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreatePeriodicBSpline|Periodic B-spline by control points]]: Creates a periodic (closed) B-spline curve from control points. |
|||
<!--T:169--> |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_CreateBSplineByInterpolation.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateBSplineByInterpolation|B-spline by knots]]: Creates a B-spline curve through knot points. {{Version|0.21}} |
|||
<!--T:170--> |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_CreatePeriodicBSplineByInterpolation.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreatePeriodicBSplineByInterpolation|Periodic B-spline by knots]]: Creates a periodic (closed) B-spline curve through knot points. {{Version|0.21}} |
|||
<!--T:42--> |
<!--T:42--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CreatePolyline.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreatePolyline|Polyline |
* [[Image:Sketcher_CreatePolyline.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreatePolyline|Polyline]]: Creates a series of line and arc segments connected by their endpoints. The tool has several modes. |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:184--> |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCreateRectangles">[[Image:Sketcher_CreateRectangle.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Create rectangle:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCreateRectangles pages redirect here--> |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CompCreateRectangles.png|48px]] [[Sketcher_CompCreateRectangles|Create a rectangle]]: This is an icon menu in the Sketcher toolbar that holds the following commands: {{Version|0.20}} |
|||
<!--T:43--> |
<!--T:43--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateRectangle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateRectangle|Rectangle]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateRectangle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateRectangle|Rectangle]]: Creates a rectangle. {{Version|0.22}}: The tool has four modes. Rounded corners and creating an offset copy are optional features. |
||
<!--T:136--> |
<!--T:136--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateRectangle_Center.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateRectangle_Center|Centered rectangle]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateRectangle_Center.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateRectangle_Center|Centered rectangle]]: Creates a centered rectangle. {{Version|0.22}}: This is the same tool as [[Sketcher_CreateRectangle|Rectangle]] but with a different initial mode. |
||
<!--T:137--> |
<!--T:137--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateOblong.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateOblong|Rounded rectangle]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateOblong.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateOblong|Rounded rectangle]]: Creates a rounded rectangle. Idem. |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:185--> |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCreateRegularPolygon">[[Image:Sketcher_CreateHexagon.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Create regular polygon:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCreateRegularPolygon pages redirect here--> |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CompCreateRegularPolygon.png|48px]] [[Sketcher_CompCreateRegularPolygon|Create a regular polygon]]: This is an icon menu in the Sketcher toolbar that holds the following commands: |
|||
<!--T:44--> |
<!--T:44--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateTriangle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateTriangle|Triangle]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateTriangle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateTriangle|Triangle]]: creates an equilateral triangle. {{Version|0.22}}: This is the same tool as [[Sketcher_CreateRegularPolygon|Regular polygon]] but with the number of sides preset to a specif value. |
||
<!--T:45--> |
<!--T:45--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateSquare.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateSquare|Square]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateSquare.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateSquare|Square]]: Creates a square. Idem. |
||
<!--T:46--> |
<!--T:46--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreatePentagon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreatePentagon|Pentagon]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreatePentagon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreatePentagon|Pentagon]]: Creates a pentagon. Idem. |
||
<!--T:47--> |
<!--T:47--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateHexagon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateHexagon|Hexagon]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateHexagon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateHexagon|Hexagon]]: Creates a hexagon. Idem. |
||
<!--T:48--> |
<!--T:48--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateHeptagon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateHeptagon|Heptagon]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateHeptagon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateHeptagon|Heptagon]]: Creates a heptagon. Idem. |
||
<!--T:49--> |
<!--T:49--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateOctagon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateOctagon|Octagon]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateOctagon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateOctagon|Octagon]]: Creates an octagon. Idem. |
||
<!--T:118--> |
<!--T:118--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateRegularPolygon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateRegularPolygon|Regular polygon]] |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateRegularPolygon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateRegularPolygon|Regular polygon]]: Creates a regular polygon. The number of sides can be specified. |
||
<!--T:186--> |
|||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompSlot">[[Image:Sketcher_CreateSlot.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Create slot:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompSlot pages redirect here--> |
|||
<!--T:50--> |
<!--T:50--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateSlot.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateSlot|Slot]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateSlot.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateSlot|Slot]]: Creates a slot. |
||
<!--T:178--> |
|||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateArcSlot.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateArcSlot|Arc slot]]: Creates an arc slot. {{Version|0.22}} |
|||
<!--T:187--> |
|||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCreateFillets">[[Image:Sketcher_CreateFillet.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Create fillet/chamfer:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCreateFillets pages redirect here--> |
|||
<!--T:51--> |
<!--T:51--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateFillet.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateFillet|Fillet]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateFillet.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateFillet|Fillet]]: Creates a fillet between two non-parallel edges. {{Version|0.22}}: The tool can also create a chamfer. |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:236--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateChamfer.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateChamfer|Chamfer]]: creates a chamfer between two non-parallel edges. This is the same tool as [[Sketcher_CreateFillet|Fillet]] but with a different initial mode. {{Version|0.22}} |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_Trimming.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Trimming|Trim]]: Trims a line, circle or arc with respect to the clicked point. |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:188--> |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCurveEdition">[[Image:Sketcher_Trimming.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Edit edge:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCurveEdition pages redirect here--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_Extend.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Extend|Extend]]: Extends a line or an arc to a boundary line, arc, ellipse, arc of ellipse or a point in space. |
|||
<!--T:52--> |
|||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_Trimming.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Trimming|Trim]]: Trims an edge at the nearest intersections with other edges. |
|||
<!--T:134--> |
<!--T:134--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_Split.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Split|Split]]: Splits |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_Split.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Split|Split]]: Splits an edge while transferring most constraints. |
||
<!--T:115--> |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_Extend.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Extend|Extend]]: Extends or shortens a line or an arc to an arbitrary location, or to a target edge or point. |
|||
<!--T:53--> |
<!--T:53--> |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_External.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_External|External geometry]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_External.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_External|External geometry]]: Projects edges and/or vertices belonging to objects outside the sketch onto the sketch plane. |
||
<!--T:116--> |
<!--T:116--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_CarbonCopy.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CarbonCopy|Carbon copy]]: Copies |
* [[File:Sketcher_CarbonCopy.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CarbonCopy|Carbon copy]]: Copies all geometry and constraints from another sketch into the active sketch. |
||
<!--T:54--> |
<!--T:54--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ToggleConstruction.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ToggleConstruction|Toggle construction geometry]]: |
* [[File:Sketcher_ToggleConstruction.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ToggleConstruction|Toggle construction geometry]]: Either toggles the geometry creation tools to/from construction mode, or toggles selected geometry to/from construction geometry. |
||
===Sketcher constraints=== <!--T:55--> |
===Sketcher constraints=== <!--T:55--> |
||
| Line 239: | Line 378: | ||
Constraints are used to define lengths, set rules between sketch elements, and to lock the sketch along the vertical and horizontal axes. Some constraints require use of [[Sketcher_helper_constraint|Helper constraints]]. |
Constraints are used to define lengths, set rules between sketch elements, and to lock the sketch along the vertical and horizontal axes. Some constraints require use of [[Sketcher_helper_constraint|Helper constraints]]. |
||
<!--T:196--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainCoincidentUnified.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainCoincidentUnified|Coincident (unified)]]: Can replace the [[Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident|Coincident]] and [[Sketcher_ConstrainPointOnObject|Point on object]] constraints. {{Version|0.22}} |
|||
<!--T:57--> |
|||
These constraints are not associated with numeric data. |
|||
<!--T:58--> |
<!--T:58--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident|Coincident]]: Affixes a point onto (coincident with) one or more other points. |
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident|Coincident]]: Affixes a point onto (coincident with) one or more other points. It acts as a concentric constraint if two or more circles, arcs, ellipses or arcs of ellipses are selected. |
||
<!--T:59--> |
<!--T:59--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainPointOnObject.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainPointOnObject|Point on object]]: Affixes a point onto another object such as a line, arc, or axis. |
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainPointOnObject.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainPointOnObject|Point on object]]: Affixes a point onto another object such as a line, arc, or axis. |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:189--> |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompHorVer">[[Image:Sketcher_ConstrainHorVer.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]]Horizontal/Vertical constraints:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompHorVer pages redirect here--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainVertical.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainVertical|Vertical]]: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true vertical orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint. |
|||
<!--T:190--> |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainHorVer.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainHorVer|Horizontal/Vertical]]: Automatically applies [[Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal|Horizontal]] or [[Sketcher_ConstrainVertical|Vertical]] constraint depending on the orientation of a line. {{Version|0.22}} |
|||
<!--T:61--> |
<!--T:61--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal|Horizontal]]: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true horizontal orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint. |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal|Horizontal]]: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true horizontal orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint. |
||
<!--T:60--> |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainVertical.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainVertical|Vertical]]: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true vertical orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint. |
|||
<!--T:62--> |
<!--T:62--> |
||
| Line 274: | Line 417: | ||
* [[Image:Sketcher_ConstrainBlock.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainBlock|Block]]: it blocks an edge from moving, that is, it prevents its vertices from changing their current positions. It should be particularly useful to fix the position of B-Splines. See the [https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=26572 Block Constraint forum topic]. |
* [[Image:Sketcher_ConstrainBlock.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainBlock|Block]]: it blocks an edge from moving, that is, it prevents its vertices from changing their current positions. It should be particularly useful to fix the position of B-Splines. See the [https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=26572 Block Constraint forum topic]. |
||
<!--T:191--> |
|||
==== Dimensional constraints ==== <!--T:146--> |
|||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompDimensionTools">[[Image:Sketcher_Dimension.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Dimensional constraints:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompDimensionTools pages redirect here--> |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:192--> |
||
:* [[File:Sketcher_Dimension.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Dimension|Dimension]]: Provides context-sensitive dimensional constraint tool. {{Version|0.22}} |
|||
These are constraints associated with numeric data, for which you can use the [[Expressions|expressions]]. The data may be taken from a [[Spreadsheet_Workbench|spreadsheet]]. |
|||
<!--T:69--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainLock.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainLock|Lock]]: Constrains the selected item by setting vertical and horizontal distances relative to the origin, thereby locking the location of that item. These constraint distances can be edited later. |
|||
<!--T:70--> |
<!--T:70--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX|Horizontal distance]]: Fixes the horizontal distance between two points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin. |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX|Horizontal distance]]: Fixes the horizontal distance between two points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin. |
||
<!--T:71--> |
<!--T:71--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceY.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceY|Vertical distance]]: Fixes the vertical distance between 2 points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin. |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceY.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceY|Vertical distance]]: Fixes the vertical distance between 2 points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin. |
||
<!--T:72--> |
<!--T:72--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistance.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistance|Distance]]: Defines the |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistance.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistance|Distance]]: Defines the length of a line, the perpendicular distance between a point and a line, the distance between two points, or, {{Version|0.21}}, the distance between the edges of two circles. |
||
<!--T:159--> |
|||
* [[Image:Sketcher_CompConstrainRadDia.png|48px]] [[Sketcher_CompConstrainRadDia|Constrain arc or circle]]: This is an icon menu in the Sketcher constraints toolbar that holds the following commands: |
|||
:* <span id="Sketcher_CompConstrainRadDia">[[File:Sketcher_ConstrainRadiam.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainRadiam|Auto radius/diameter]]: Defines the radius of an arc, the diameter of a circle or the weight of a B-spline pole.</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompConstrainRadDia pages redirect here--> |
|||
<!--T:73--> |
<!--T:73--> |
||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainRadius.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainRadius|Radius]]: Defines the radius of |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainRadius.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainRadius|Radius]]: Defines the radius of an arc or circle or the weight of a B-spline pole. |
||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDiameter.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDiameter|Diameter]]: Defines the diameter of a selected arc or circle by constraining the diameter. |
|||
<!--T:158--> |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainRadiam.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainRadiam|Radiam]]: Automatically defines radius/diameter of a selected arc or circle (weight for a B-spline pole, diameter for a complete circle, radius for an arc) {{Version|0.20}} |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDiameter.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDiameter|Diameter]]: Defines the diameter of an arc or circle. |
|||
<!--T:160--> |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainAngle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainAngle|Angle]]: Defines the internal angle between two selected lines. |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainAngle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainAngle|Angle]]: Defines the internal angle between two selected lines. |
||
<!--T:69--> |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainLock.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainLock|Lock]]: Constrains the selected item by setting vertical and horizontal distances relative to the origin, thereby locking the location of that item. These constraint distances can be edited later. |
|||
==== Special constraints ==== <!--T:130--> |
==== Special constraints ==== <!--T:130--> |
||
<!--T:74--> |
<!--T:74--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainSnellsLaw.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainSnellsLaw|Snell's law]]: Constrains two lines to obey a refraction law to simulate the light going through an interface. |
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainSnellsLaw.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainSnellsLaw|Refraction (Snell's law)]]: Constrains two lines to obey a refraction law to simulate the light going through an interface. |
||
<!--T:75--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainInternalAlignment.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainInternalAlignment|Internal alignment]]: Aligns selected elements to selected shape (e.g. a line to become major axis of an ellipse). |
|||
==== Constraint tools ==== <!--T:147--> |
==== Constraint tools ==== <!--T:147--> |
||
| Line 319: | Line 461: | ||
<!--T:124--> |
<!--T:124--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ToggleActiveConstraint.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ToggleActiveConstraint|Activate/deactivate constraint]]: Enable or disable an already placed constraint. |
* [[File:Sketcher_ToggleActiveConstraint.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ToggleActiveConstraint|Activate/deactivate constraint]]: Enable or disable an already placed constraint. |
||
===Sketcher tools=== <!--T:77--> |
===Sketcher tools=== <!--T:77--> |
||
<!--T:78--> |
<!--T:78--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectElementsWithDoFs.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectElementsWithDoFs|Select unconstrained DoF]]: Highlights in green the geometry with degrees of freedom ( |
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectElementsWithDoFs.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectElementsWithDoFs|Select unconstrained DoF]]: Highlights in green the geometry with degrees of freedom (DoFs), i.e. not fully constrained. |
||
<!--T:79--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_CloseShape.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CloseShape|Close shape]]: Creates a closed shape by applying coincident constraints to endpoints. This tool is obsolete, it will not be available in future releases ({{VersionPlus|1.0}}). |
|||
<!--T:80--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConnectLines.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConnectLines|Connect edges]]: Connect sketcher elements by applying coincident constraints to endpoints. This tool is obsolete, it will not be available in future releases ({{VersionPlus|1.0}}). |
|||
<!--T:81--> |
<!--T:81--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectConstraints|Select associated constraints]]: Selects the constraints of a |
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectConstraints|Select associated constraints]]: Selects the constraints of a Sketcher element. |
||
<!--T:87--> |
<!--T:87--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectElementsAssociatedWithConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectElementsAssociatedWithConstraints|Select associated geometry]]: Select |
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectElementsAssociatedWithConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectElementsAssociatedWithConstraints|Select associated geometry]]: Select Sketcher elements associated with constraints. |
||
<!--T:85--> |
<!--T:85--> |
||
| Line 349: | Line 485: | ||
<!--T:82--> |
<!--T:82--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectOrigin.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectOrigin|Select origin]]: Selects the origin of a sketch. |
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectOrigin.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectOrigin|Select origin]]: Selects the origin of a sketch. |
||
<!--T:84--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectHorizontalAxis.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectHorizontalAxis|Select horizontal axis]]: Selects the horizontal axis of a sketch. |
|||
<!--T:83--> |
<!--T:83--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectVerticalAxis.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectVerticalAxis|Select vertical axis]]: Selects the vertical axis of a sketch. |
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectVerticalAxis.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectVerticalAxis|Select vertical axis]]: Selects the vertical axis of a sketch. |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:179--> |
||
* [[File: |
* [[File:Sketcher_Offset.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Offset|Offset geometry]]: Adds an equidistant outline around selected edges. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:193--> |
||
* [[File: |
* [[File:Sketcher_Rotate.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Rotate|Polar transform]]: Rotates and optionally copies (to create polar patterns) selected geometries. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:237--> |
||
* [[File: |
* [[File:Sketcher_Scale.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Scale|Scale transform]]: Scales and optionally copies selected geometries. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:90--> |
||
* [[File: |
* [[File:Sketcher_Symmetry.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Symmetry|Symmetry]]: Copies a Sketcher element symmetrically to a chosen line. |
||
<!--T: |
<!--T:238--> |
||
* [[File: |
* [[File:Sketcher_Translate.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Translate|Array transform]]: Translates and optionally copies (to create linear patterns) selected geometries. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
<!--T:94--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_RectangularArray.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_RectangularArray|Rectangular array]]: Creates an array of selected sketcher elements. |
|||
<!--T:138--> |
<!--T:138--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_RemoveAxesAlignment.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_RemoveAxesAlignment|Remove axes alignment]]: Remove axes alignment while trying to preserve the constraint relationship of the selection. |
* [[File:Sketcher_RemoveAxesAlignment.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_RemoveAxesAlignment|Remove axes alignment]]: Remove axes alignment while trying to preserve the constraint relationship of the selection. |
||
<!--T:95--> |
<!--T:95--> |
||
| Line 380: | Line 516: | ||
* [[File:Sketcher_DeleteAllConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_DeleteAllConstraints|Delete all constraints]]: Deletes all constraints from the sketch. |
* [[File:Sketcher_DeleteAllConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_DeleteAllConstraints|Delete all constraints]]: Deletes all constraints from the sketch. |
||
<!--T:239--> |
|||
* <span id="Sketcher_CopyClipboard">[[File:Edit-copy.svg|32px]] Copy in Sketcher: See [[#Copy,_cut_and_paste|Copy, cut and paste]].</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CopyClipboard pages redirect here--> |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:240--> |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_Cut">[[File:Edit-cut.svg|32px]] Cut in Sketcher: See [[#Copy,_cut_and_paste|Copy, cut and paste]].</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_Cut pages redirect here--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineDegree.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineDegree|Show/hide B-spline degree]] |
|||
<!--T: |
<!--T:241--> |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_Paste">[[File:Edit-paste.svg|32px]] Paste in Sketcher: See [[#Copy,_cut_and_paste|Copy, cut and paste]].</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_Paste pages redirect here--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplinePolygon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplinePolygon|Show/hide B-spline control polygon]] |
|||
<!--T: |
===Sketcher B-spline tools=== <!--T:97--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineComb.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineComb|Show/hide B-spline curvature comb]] |
|||
<!--T:101--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineKnotMultiplicity.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineKnotMultiplicity|Show/hide B-spline knot multiplicity]] |
|||
<!--T:129--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplinePoleWeight.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplinePoleWeight|Show/hide B-spline control point weight]], {{Version|0.19}} |
|||
<!--T:102--> |
<!--T:102--> |
||
* [[File: |
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineConvertToNURBS.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineConvertToNURBS|Convert geometry to B-spline]]: Converts compatible geometry, edges and curves, into a B-spline. |
||
<!--T:103--> |
<!--T:103--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseDegree.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseDegree|Increase B-spline degree]] |
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseDegree.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseDegree|Increase B-spline degree]]: Increases the degree (order) of a B-spline. |
||
<!--T:128--> |
<!--T:128--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineDecreaseDegree.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineDecreaseDegree|Decrease B-spline degree]] |
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineDecreaseDegree.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineDecreaseDegree|Decrease B-spline degree]]: Decreases the degree (order) of a B-spline. |
||
<!--T:104--> |
<!--T:104--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseKnotMultiplicity.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseKnotMultiplicity|Increase knot multiplicity]] |
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseKnotMultiplicity.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseKnotMultiplicity|Increase knot multiplicity]]: Increases the multiplicity of a B-spline knot. |
||
<!--T:105--> |
<!--T:105--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineDecreaseKnotMultiplicity.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineDecreaseKnotMultiplicity|Decrease knot multiplicity]] |
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineDecreaseKnotMultiplicity.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineDecreaseKnotMultiplicity|Decrease knot multiplicity]]: Decreases the multiplicity of a B-spline knot. |
||
<!--T:149--> |
<!--T:149--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineInsertKnot.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineInsertKnot|Insert knot]] |
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineInsertKnot.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineInsertKnot|Insert knot]]: Inserts a knot into an existing B-spline. |
||
<!--T:163--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_JoinCurves.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_JoinCurves|Join curves]]: Joins two curves at selected end points. {{Version|0.21}} |
|||
===Sketcher visual=== <!--T:194--> |
|||
<!--T:107--> |
<!--T:107--> |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_SwitchVirtualSpace.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SwitchVirtualSpace|Switch virtual space]]: Allows you to hide all constraints of a sketch and make them visible again. |
* [[File:Sketcher_SwitchVirtualSpace.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SwitchVirtualSpace|Switch virtual space]]: Allows you to hide all constraints of a sketch and make them visible again. |
||
<!--T:98--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineDegree.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineDegree|Show/hide B-spline degree]]: Shows or hides the display of the degree of a B-spline. |
|||
<!--T:99--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplinePolygon.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplinePolygon|Show/hide B-spline control polygon]]: Shows or hides the display of the defining polygon of a B-spline. |
|||
<!--T:100--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineComb.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineComb|Show/hide B-spline curvature comb]]: Shows or hides the display of the curvature comb of a B-spline. |
|||
<!--T:101--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineKnotMultiplicity.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineKnotMultiplicity|Show/hide B-spline knot multiplicity]]: Shows or hides the display of the knot multiplicity of a B-spline. |
|||
<!--T:129--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplinePoleWeight.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplinePoleWeight|Show/hide B-spline control point weight]]: Shows or hides the display of the weights for the control points of a B-spline. |
|||
<!--T:195--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_ArcOverlay.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ArcOverlay|Show/hide circular helper for arcs]]: Shows or hides the circular helpers (circle outlines) for arcs. {{Version|0.22}} |
|||
===Obsolete tools=== <!--T:173--> |
|||
<!--T:91--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_Clone.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Clone|Clone]]: Clones a Sketcher element. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.22}}. |
|||
<!--T:79--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_CloseShape.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CloseShape|Close shape]]: Creates a closed shape by applying coincident constraints to endpoints. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.21}}. |
|||
<!--T:162--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_CreatePointFillet.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreatePointFillet|Corner-preserving fillet]]: Creates a fillet between two non-parallel lines while preserving their corner point. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.22}}. |
|||
<!--T:80--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConnectLines.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConnectLines|Connect edges]]: Connect Sketcher elements by applying coincident constraints to endpoints. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.21}}. |
|||
<!--T:92--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_Copy.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Copy|Copy]]: Copies a Sketcher element. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.22}}. |
|||
<!--T:93--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_Move.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Move|Move]]: Moves the selected geometry taking as reference the last selected point. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.22}}. |
|||
<!--T:94--> |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_RectangularArray.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_RectangularArray|Rectangular array]]: Creates an array of selected Sketcher elements. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.22}}. |
|||
== Preferences == <!--T:108--> |
== Preferences == <!--T:108--> |
||
<!--T:109--> |
<!--T:109--> |
||
* [[Image: |
* [[Image:Workbench_Sketcher.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Preferences|Preferences]]: Preferences for the Sketcher Workbench. |
||
== Best |
== Best practices == <!--T:148--> |
||
<!--T:14--> |
<!--T:14--> |
||
Every CAD user develops |
Every CAD user develops their own way of working over time, but there are some useful general principles to follow. |
||
<!--T:15--> |
<!--T:15--> |
||
* A series of simple sketches is easier to manage than a single complex one. For example, a first sketch can be created for the base 3D feature (either a pad or a revolve), while a second one can contain holes or cutouts (pockets). Some details can be left out, to be realized later on as 3D features. You can choose to avoid fillets in your sketch if there are too many, and add them as a 3D feature. |
* A series of simple sketches is easier to manage than a single complex one. For example, a first sketch can be created for the base 3D feature (either a pad or a revolve), while a second one can contain holes or cutouts (pockets). Some details can be left out, to be realized later on as 3D features. You can choose to avoid fillets in your sketch if there are too many, and add them as a 3D feature. |
||
* Always create a closed profile, or your sketch won't produce a solid, but rather a set of open faces. If you don't want some of the objects to be included in the solid creation, turn them to construction elements with the Construction Mode tool. |
* Always create a closed profile, or your sketch won't produce a solid, but rather a set of open faces. If you don't want some of the objects to be included in the solid creation, turn them to construction elements with the Construction Mode tool. |
||
* Use the |
* Use the Auto constraints feature to limit the number of constraints you'll have to add manually. |
||
* As a general rule, apply geometric constraints first, then dimensional constraints, and lock your sketch last. But remember: rules are made to be broken. If you're having trouble manipulating your sketch, it may be useful to constrain a few objects first before completing your profile. |
* As a general rule, apply geometric constraints first, then dimensional constraints, and lock your sketch last. But remember: rules are made to be broken. If you're having trouble manipulating your sketch, it may be useful to constrain a few objects first before completing your profile. |
||
* If possible, center your sketch to the origin (0,0) with the |
* If possible, center your sketch to the origin (0,0) with the Lock constraint. If your sketch is not symmetric, locate one of its points to the origin, or choose nice round numbers for the lock distances. |
||
* If you have the possibility to choose between the Length constraint and the Horizontal or Vertical |
* If you have the possibility to choose between the Length constraint and the Horizontal or Vertical distance constraints, prefer the latter. Horizontal and Vertical distance constraints are computationally cheaper. |
||
* In general, the best constraints to use are: Horizontal and Vertical |
* In general, the best constraints to use are: Horizontal and Vertical constraints; Horizontal and Vertical length constraints; point-to-point Tangency. If possible, limit the use of these: the general Length constraint; edge-to-edge Tangency; Point on object constraint; Symmetric constraint. |
||
* If in doubt about the validity of a sketch once it is complete (features turn green), close the Sketcher dialog |
* If in doubt about the validity of a sketch once it is complete (features turn green), close the Sketcher dialog and use [[File:Sketcher_ValidateSketch.svg|24px]] [[Sketcher_ValidateSketch|Validate sketch]]. |
||
== Tutorials == <!--T:19--> |
== Tutorials == <!--T:19--> |
||
<!--T:121--> |
<!--T:121--> |
||
* [https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=36&t=30104 Sketcher |
* [https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=36&t=30104 Sketcher Lecture] by chrisb. This is a more than 80 page PDF document that serves as a detailed manual for the Sketcher. It explains the basics of Sketcher usage, and goes into a lot of detail about the creation of geometrical shapes, and each of the constraints. |
||
* [[ |
* [[Basic_Sketcher_Tutorial|Basic Sketcher Tutorial]] for beginners |
||
* [[ |
* [[Sketcher_Micro_Tutorial_-_Constraint_Practices|Sketcher Micro Tutorial - Constraint Practices]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[Sketcher_requirement_for_a_sketch|Sketcher requirement for a sketch]] Minimum requirement for a sketch and Complete determination of a sketch |
||
== Scripting == <!--T:132--> |
== Scripting == <!--T:132--> |
||
| Line 452: | Line 626: | ||
<!--T:133--> |
<!--T:133--> |
||
The [[Sketcher_scripting|Sketcher scripting]] page contains examples on how to create constraints from Python scripts. |
The [[Sketcher_scripting|Sketcher scripting]] page contains examples on how to create constraints from Python scripts. |
||
== Examples == <!--T:171--> |
|||
<!--T:172--> |
|||
For some ideas of what can be achieved with Sketcher tools, have a look at: [[Sketcher_Examples|Sketcher examples]]. |
|||
</translate> |
|||
[[Image:Sketcher_ExampleHinge-01.gif|80px|link=]] |
|||
[[Image:Sketcher ExampleHinge-15.png|90px|link=]] |
|||
<translate> |
|||
Latest revision as of 16:40, 15 April 2024

Introduction
With the FreeCAD Sketcher Workbench 2D sketches intended for use in other workbenches can be created. 2D sketches are the starting point for many CAD models. They typically define the profiles and paths for operations to create 3D shapes. A model may depend on several sketches for its final shape.
Together with boolean operations defined in the Part Workbench, the Sketcher Workbench, or "The Sketcher" for short, forms the basis of the constructive solid geometry (CSG) method of building solids. Together with
PartDesign Workbench operations, it also forms the basis of the feature editing methodology of creating solids. But many other workbenches use sketches as well.
The Sketcher workbench features constraints, allowing 2D shapes to follow precise geometrical definitions in terms of length, angles, and relationships (horizontality, verticality, perpendicularity, etc.). A constraint solver calculates the constrained-extent of 2D geometry and allows interactive exploration of the degrees-of-freedom of the sketch.
The Sketcher is not intended for producing 2D blueprints. Once sketches are used to generate a solid feature, they are automatically hidden and Constraints are only visible in Sketch edit mode. If you only need to produce 2D views for print, and don't want to create 3D models, check out the Draft workbench.
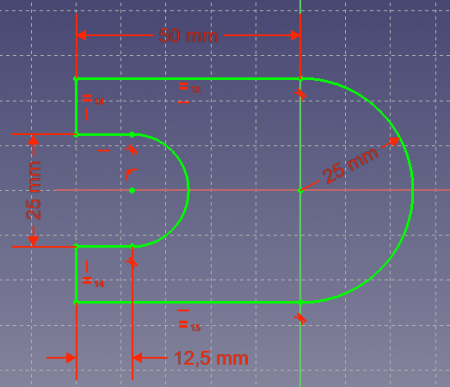
A fully constrained sketch
Constraints
Constraints are used to limit the degrees of freedom of an object. For example, a line without constraints has 4 Degrees Of Freedom (abbreviated as "DoF"): it can be moved horizontally or vertically, it can be stretched, and it can be rotated.
Applying a horizontal or vertical constraint, or an angle constraint (relative to another line or to one of the axes), will limit its capacity to rotate, thus leaving it with 3 degrees of freedom. Locking one of its points in relation to the origin will remove another 2 degrees of freedom. And applying a dimension constraint will remove the last degree of freedom. The line is then considered fully-constrained.
Objects can be constrained in relation to one another. Two lines can be joined through one of their points with the coincident point constraint. An angle can be set between them, or they can be set perpendicular. A line can be tangent to an arc or a circle, and so on. A complex Sketch with multiple objects may have a number of different solutions, and making it fully-constrained can mean that just one of these possible solutions has been reached based on the applied constraints.
There are two kinds of constraints: geometric and dimensional. They are detailed in the Tools section below.
Driving vs. reference constraints
Edit constraints
When a driving constraint is created, and if the Ask for value after creating a dimensional constraint preference is selected (default), a dialog opens to edit its value.
You can enter a numerical value or an expression, and it is possible to name the constraint to facilitate its use in other expressions. You can also check the Reference checkbox to switch the constrain to reference mode.
To edit the value of an existing dimensional constraint do one of the following:
- Double-click the constraint value in the 3D view.
- Double-click the constraint in the Sketcher Dialog.
- Right-click the constraint in the Sketcher Dialog and select the Change value option from the context menu.
Reposition constraints
Constraints can be repositioned in the 3D view by dragging. Hold down the left mouse button over the constraint value and move the mouse.
Profile sketches
To create a sketch that can be used as a profile for generating solids certain rules must be followed:
- The sketch must contain only closed contours. Gaps between endpoints, however small, are not allowed.
- Contours can be nested, to create voids, but should not self-intersect or intersect other contours.
- Contours cannot share edges with other contours. Duplicate edges should be avoided.
- T-connections, that is more than two edges sharing a common point, or a point touching an edge, are not allowed.
These rules do not apply to construction geometry (default color blue), which is not shown outside edit mode, or if the sketch is used for a different purpose. Depending on the workbench and the tool that will use the profile sketch, additional restrictions may apply.
Drawing aids
The Sketcher Workbench has several drawing aids and other features that can help when creating geometry and applying constraints.
Continue modes
There are two continue modes: Geometry creation "Continue Mode" and Constraint creation "Continue Mode". If these are checked (default) in the preferences, related tools will restart after finishing. To exit an continuous tool press Esc or the right mouse button. This must be repeated if a continuous geometry tool has already received input. You can also exit a continuous tool by starting another geometry or constraint creation tool. Note that pressing Esc if no tool is active will exit sketch edit mode. Uncheck the Esc can leave sketch edit mode preference if you often inadvertently press Esc too many times.
Auto constraints
In sketches that have Auto constraints checked (default) several constraints are applied automatically when hovering the cursor properly (their symbols are displayed next to the cursor before applying). This is a per-sketch setting that can be changed in the Sketcher Dialog or by changing the ViewAutoconstraints property of the sketch. The following constraints are applied automatically:
- Coincident
- Point on object
- Horizontal
- Vertical
- Tangent
- introduced in version 0.22: Symmetric (line midpoint)
Snapping
It is possible to snap to grid lines and grid intersection, to edges of geometry and midpoints of lines and arcs, and to certain angles. Please note that snapping does not produce constraints in and of itself. For example, only if Auto constraints is switched on will snapping to an edge produce a Point on object constraint. But just picking a point on the edge would then have the same result.
On-View-Parameters
Depending on the selected option in the preferences only the dimensional On-View-Parameters or both the dimensional and the positional On-View-Parameters can be enabled. Positional parameters allow the input of exact coordinates, for example the center of a circle, or the start point of a line. Dimensional parameters allow the input of exact dimensions, for example the radius of a circle, or the length and angle of a line. On-View-Parameters are not available for all tools.
Determining the center point of a circle with the positional parameters enabled
Determining the radius of a circle with the dimensional parameters enabled
If values are entered and confirmed by pressing Enter or Tab, related constraints are added automatically. If two parameters are displayed at the same time, for example the X and Y coordinate of a point, it is possible to enter one value and pick a point to define the other. Depending on the object additional constraints may be required to fully constrain it. Constraints resulting from On-View-Parameters take precedence over those that may result from Auto constraints.
Arc created by entering all On-View-Parameters with resulting automatically created constraints
Coordinate display
If the Show coordinates beside cursor while editing preference is checked (default), the parameters of the current geometry tool (coordinates, radius, or length and angle) are displayed next to the cursor. This is deactivated while On-View-Parameters are shown.
Selection
No need for Ctrl, but... Select in Sketcher Dialog...
Box selection
Connected geometry selection
Copy, cut and paste
The standard keyboard shortcuts can be used to copy, Ctrl+C, cut, Ctrl+X, and paste, Ctrl+V, the currently selected Sketcher geometry including related constraints. But these tools are also available from the Sketch → Sketcher tools menu. They can be used within the same sketch but also between different sketches or separate instances of FreeCAD. Since the data is copied to the clipboard in the form of Python code, it can be used in other ways too (e.g. shared on the forum).
Tools
The Sketcher Workbench tools are located in the Sketch menu and/or several toolbars. introduced in version 0.21: Almost all Sketcher toolbars are only displayed while a sketch is in edit mode. The only exception is the Sketcher toolbar which is only displayed if no sketch is in edit mode.
introduced in version 0.21: If a sketch is in edit mode the Structure toolbar is hidden as none of its tools can then be used.
General
Sketcher toolbar
Create sketch: Creates a new sketch and opens the Sketcher Dialog to edit it.
Edit sketch: Opens the Sketcher Dialog to edit an existing sketch.
Attach sketch: Attaches a sketch to selected geometry.
Reorient sketch: Places a sketch on one of the main planes with an optional offset. It can also be used to detach a sketch.
Validate sketch: Can analyze and repair a sketch that is no longer editable or has invalid constraints, or add missing coincident constraints.
Merge sketches: Merges two or more sketches.
Mirror sketch: Mirrors sketches along their X axis, Y axis, or origin.
Sketcher Edit Mode toolbar
Leave sketch: Finishes sketch edit mode and closes the Sketcher Dialog.
View sketch: Sets the 3D view perpendicular to the sketch plane.
View section: Toggles a temporary section plane that hides any objects and parts of objects in front of the sketch plane.
Sketcher edit tools toolbar
Toggle grid: Toggles the grid in the sketch currently being edited. Settings can be changed in the related menu. introduced in version 0.21
Toggle snap: Toggles snapping in all sketches. Settings can be changed in the related menu. introduced in version 0.21
Configure rendering order: The rendering order of all sketches can be changed in the related menu. introduced in version 0.21
Other
Stop operation: Stops any currently running geometry or constraint creation tool.
Sketcher geometries
These are tools for creating objects.
Point: Creates a point.
Line: Creates a line. introduced in version 0.22: The tool has three modes.
Arc by center: Creates an arc by its center and its endpoints. introduced in version 0.22: Or by its endpoints and a point along the arc.
Arc by 3 points: Creates an arc by its endpoints and a point along the arc. introduced in version 0.22: This is the same tool as Arc by center but with a different initial mode.
Circle by center: Creates a circle by its center and a point along the circle. introduced in version 0.22: Or by three points along the circle.
Circle by 3 points: Creates a circle by three points along the circle. introduced in version 0.22: This is the same tool as Circle by center but with a different initial mode.
- Ellipses, hyperbolas and parabolas are called "conics" because they are types of conic sections.
Ellipse by center: Creates an ellipse by its center, an endpoint of one of its axes, and a point along the ellipse. introduced in version 0.22: Or by both endpoints of one of its axes and a point along the ellipse.
Ellipse by 3 points: Creates an ellipse by the endpoints of one of its axes and a point along the ellipse. introduced in version 0.22: This is the same tool as Ellipse by center but with a different initial mode.
Arc of ellipse: Creates an arc of ellipse.
Arc of hyperbola: Creates an arc of hyperbola.
Arc of parabola: Creates an arc of parabola.
B-spline by control points: Creates a B-spline curve from control points.
Periodic B-spline by control points: Creates a periodic (closed) B-spline curve from control points.
B-spline by knots: Creates a B-spline curve through knot points. introduced in version 0.21
Periodic B-spline by knots: Creates a periodic (closed) B-spline curve through knot points. introduced in version 0.21
Polyline: Creates a series of line and arc segments connected by their endpoints. The tool has several modes.
Rectangle: Creates a rectangle. introduced in version 0.22: The tool has four modes. Rounded corners and creating an offset copy are optional features.
Centered rectangle: Creates a centered rectangle. introduced in version 0.22: This is the same tool as Rectangle but with a different initial mode.
Rounded rectangle: Creates a rounded rectangle. Idem.
Triangle: creates an equilateral triangle. introduced in version 0.22: This is the same tool as Regular polygon but with the number of sides preset to a specif value.
Square: Creates a square. Idem.
Pentagon: Creates a pentagon. Idem.
Hexagon: Creates a hexagon. Idem.
Heptagon: Creates a heptagon. Idem.
Octagon: Creates an octagon. Idem.
Regular polygon: Creates a regular polygon. The number of sides can be specified.
Slot: Creates a slot.
Arc slot: Creates an arc slot. introduced in version 0.22
Fillet: Creates a fillet between two non-parallel edges. introduced in version 0.22: The tool can also create a chamfer.
Chamfer: creates a chamfer between two non-parallel edges. This is the same tool as Fillet but with a different initial mode. introduced in version 0.22
Trim: Trims an edge at the nearest intersections with other edges.
Split: Splits an edge while transferring most constraints.
Extend: Extends or shortens a line or an arc to an arbitrary location, or to a target edge or point.
External geometry: Projects edges and/or vertices belonging to objects outside the sketch onto the sketch plane.
Carbon copy: Copies all geometry and constraints from another sketch into the active sketch.
Toggle construction geometry: Either toggles the geometry creation tools to/from construction mode, or toggles selected geometry to/from construction geometry.
Sketcher constraints
Constraints are used to define lengths, set rules between sketch elements, and to lock the sketch along the vertical and horizontal axes. Some constraints require use of Helper constraints.
Coincident (unified): Can replace the Coincident and Point on object constraints. introduced in version 0.22
Coincident: Affixes a point onto (coincident with) one or more other points. It acts as a concentric constraint if two or more circles, arcs, ellipses or arcs of ellipses are selected.
Point on object: Affixes a point onto another object such as a line, arc, or axis.
Horizontal/Vertical: Automatically applies Horizontal or Vertical constraint depending on the orientation of a line. introduced in version 0.22
Horizontal: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true horizontal orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint.
Vertical: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true vertical orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint.
Parallel: Constrains two or more lines parallel to one another.
Perpendicular: Constrains two lines perpendicular to one another, or constrains a line perpendicular to an arc endpoint.
Tangent: Creates a tangent constraint between two selected entities, or a co-linear constraint between two line segments. A line segment does not have to lie directly on an arc or circle to be constrained tangent to that arc or circle.
Equal: Constrains two selected entities equal to one another. If used on circles or arcs their radii will be set equal.
Symmetric: Constrains two points symmetrically about a line, or constrains the first two selected points symmetrically about a third selected point.
Block: it blocks an edge from moving, that is, it prevents its vertices from changing their current positions. It should be particularly useful to fix the position of B-Splines. See the Block Constraint forum topic.
Dimension: Provides context-sensitive dimensional constraint tool. introduced in version 0.22
Horizontal distance: Fixes the horizontal distance between two points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin.
Vertical distance: Fixes the vertical distance between 2 points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin.
Distance: Defines the length of a line, the perpendicular distance between a point and a line, the distance between two points, or, introduced in version 0.21, the distance between the edges of two circles.
Auto radius/diameter: Defines the radius of an arc, the diameter of a circle or the weight of a B-spline pole.
Radius: Defines the radius of an arc or circle or the weight of a B-spline pole.
Diameter: Defines the diameter of an arc or circle.
Angle: Defines the internal angle between two selected lines.
Lock: Constrains the selected item by setting vertical and horizontal distances relative to the origin, thereby locking the location of that item. These constraint distances can be edited later.
Special constraints
Refraction (Snell's law): Constrains two lines to obey a refraction law to simulate the light going through an interface.
Constraint tools
The following tools can be used the change the effect of constraints:
Toggle driving/reference constraint: Toggles the toolbar or the selected constraints to/from reference mode.
Activate/deactivate constraint: Enable or disable an already placed constraint.
Sketcher tools
Select unconstrained DoF: Highlights in green the geometry with degrees of freedom (DoFs), i.e. not fully constrained.
Select associated constraints: Selects the constraints of a Sketcher element.
Select associated geometry: Select Sketcher elements associated with constraints.
Select redundant constraints: Selects redundant constraints of a sketch.
Select conflicting constraints: Selects conflicting constraints of a sketch.
Show/hide internal geometry: Recreates missing/deletes unneeded internal geometry of a selected ellipse, arc of ellipse/hyperbola/parabola or B-spline.
Select origin: Selects the origin of a sketch.
Select horizontal axis: Selects the horizontal axis of a sketch.
Select vertical axis: Selects the vertical axis of a sketch.
Offset geometry: Adds an equidistant outline around selected edges. introduced in version 0.22
Polar transform: Rotates and optionally copies (to create polar patterns) selected geometries. introduced in version 0.22
Scale transform: Scales and optionally copies selected geometries. introduced in version 0.22
Symmetry: Copies a Sketcher element symmetrically to a chosen line.
Array transform: Translates and optionally copies (to create linear patterns) selected geometries. introduced in version 0.22
Remove axes alignment: Remove axes alignment while trying to preserve the constraint relationship of the selection.
Delete all geometry: Deletes all geometry from the sketch.
Delete all constraints: Deletes all constraints from the sketch.
Copy in Sketcher: See Copy, cut and paste.
Cut in Sketcher: See Copy, cut and paste.
Paste in Sketcher: See Copy, cut and paste.
Sketcher B-spline tools
Convert geometry to B-spline: Converts compatible geometry, edges and curves, into a B-spline.
Increase B-spline degree: Increases the degree (order) of a B-spline.
Decrease B-spline degree: Decreases the degree (order) of a B-spline.
Increase knot multiplicity: Increases the multiplicity of a B-spline knot.
Decrease knot multiplicity: Decreases the multiplicity of a B-spline knot.
Insert knot: Inserts a knot into an existing B-spline.
Join curves: Joins two curves at selected end points. introduced in version 0.21
Sketcher visual
Switch virtual space: Allows you to hide all constraints of a sketch and make them visible again.
Show/hide B-spline degree: Shows or hides the display of the degree of a B-spline.
Show/hide B-spline control polygon: Shows or hides the display of the defining polygon of a B-spline.
Show/hide B-spline curvature comb: Shows or hides the display of the curvature comb of a B-spline.
Show/hide B-spline knot multiplicity: Shows or hides the display of the knot multiplicity of a B-spline.
Show/hide B-spline control point weight: Shows or hides the display of the weights for the control points of a B-spline.
Show/hide circular helper for arcs: Shows or hides the circular helpers (circle outlines) for arcs. introduced in version 0.22
Obsolete tools
Clone: Clones a Sketcher element. Not available in version 0.22 and above.
Close shape: Creates a closed shape by applying coincident constraints to endpoints. Not available in version 0.21 and above.
Corner-preserving fillet: Creates a fillet between two non-parallel lines while preserving their corner point. Not available in version 0.22 and above.
Connect edges: Connect Sketcher elements by applying coincident constraints to endpoints. Not available in version 0.21 and above.
Copy: Copies a Sketcher element. Not available in version 0.22 and above.
Move: Moves the selected geometry taking as reference the last selected point. Not available in version 0.22 and above.
Rectangular array: Creates an array of selected Sketcher elements. Not available in version 0.22 and above.
Preferences
Preferences: Preferences for the Sketcher Workbench.
Best practices
Every CAD user develops their own way of working over time, but there are some useful general principles to follow.
- A series of simple sketches is easier to manage than a single complex one. For example, a first sketch can be created for the base 3D feature (either a pad or a revolve), while a second one can contain holes or cutouts (pockets). Some details can be left out, to be realized later on as 3D features. You can choose to avoid fillets in your sketch if there are too many, and add them as a 3D feature.
- Always create a closed profile, or your sketch won't produce a solid, but rather a set of open faces. If you don't want some of the objects to be included in the solid creation, turn them to construction elements with the Construction Mode tool.
- Use the Auto constraints feature to limit the number of constraints you'll have to add manually.
- As a general rule, apply geometric constraints first, then dimensional constraints, and lock your sketch last. But remember: rules are made to be broken. If you're having trouble manipulating your sketch, it may be useful to constrain a few objects first before completing your profile.
- If possible, center your sketch to the origin (0,0) with the Lock constraint. If your sketch is not symmetric, locate one of its points to the origin, or choose nice round numbers for the lock distances.
- If you have the possibility to choose between the Length constraint and the Horizontal or Vertical distance constraints, prefer the latter. Horizontal and Vertical distance constraints are computationally cheaper.
- In general, the best constraints to use are: Horizontal and Vertical constraints; Horizontal and Vertical length constraints; point-to-point Tangency. If possible, limit the use of these: the general Length constraint; edge-to-edge Tangency; Point on object constraint; Symmetric constraint.
- If in doubt about the validity of a sketch once it is complete (features turn green), close the Sketcher dialog and use
Validate sketch.
Tutorials
- Sketcher Lecture by chrisb. This is a more than 80 page PDF document that serves as a detailed manual for the Sketcher. It explains the basics of Sketcher usage, and goes into a lot of detail about the creation of geometrical shapes, and each of the constraints.
- Basic Sketcher Tutorial for beginners
- Sketcher Micro Tutorial - Constraint Practices
- Sketcher requirement for a sketch Minimum requirement for a sketch and Complete determination of a sketch
Scripting
The Sketcher scripting page contains examples on how to create constraints from Python scripts.
Examples
For some ideas of what can be achieved with Sketcher tools, have a look at: Sketcher examples.


- General: Create sketch, Edit sketch, Map sketch to face, Reorient sketch, Validate sketch, Merge sketches, Mirror sketch, Leave sketch, View sketch, View section, Toggle grid, Toggle snap, Configure rendering order, Stop operation
- Sketcher geometries: Point, Line, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Circle, Circle by 3 points, Ellipse, Ellipse by 3 points, Arc of ellipse, Arc of hyperbola, Arc of parabola, B-spline by control points, Periodic B-spline by control points, B-spline by knots, Periodic B-spline by knots, Polyline, Rectangle, Centered rectangle, Rounded rectangle, Triangle, Square, Pentagon, Hexagon, Heptagon, Octagon, Regular polygon, Slot, Fillet, Corner-preserving fillet, Trim, Extend, Split, External geometry, Carbon copy, Toggle construction geometry
- Sketcher constraints:
- Geometric constraints: Coincident, Point on object, Vertical, Horizontal, Parallel, Perpendicular, Tangent, Equal, Symmetric, Block
- Dimensional constraints: Lock, Horizontal distance, Vertical distance, Distance, Radius or weight, Diameter, Auto radius/diameter, Angle, Refraction (Snell's law)
- Constraint tools: Toggle driving/reference constraint, Activate/deactivate constraint
- Sketcher tools: Select unconstrained DoF, Select associated constraints, Select associated geometry, Select redundant constraints, Select conflicting constraints, Show/hide internal geometry, Select origin, Select horizontal axis, Select vertical axis, Symmetry, Clone, Copy, Move, Rectangular array, Remove axes alignment, Delete all geometry, Delete all constraints
- Sketcher B-spline tools: Show/hide B-spline degree, Show/hide B-spline control polygon, Show/hide B-spline curvature comb, Show/hide B-spline knot multiplicity, Show/hide B-spline control point weight, Convert geometry to B-spline, Increase B-spline degree, Decrease B-spline degree, Increase knot multiplicity, Decrease knot multiplicity, Insert knot, Join curves
- Sketcher virtual space: Switch virtual space
- Additional: Sketcher Dialog, Preferences, Sketcher scripting
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Start, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework, Web
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub