Draft ShapeString tutorial/it: Difference between revisions
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> |
<languages/> |
||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
{{TutorialInfo/it |
{{TutorialInfo/it |
||
|Topic= Forma da Testo (Draft) |
|Topic= Forma da Testo (Draft) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
|Files=[https://github.com/FreeCAD/Examples/blob/master/Draft_Shapestring_Tutorial_Examples/Draft_Shapestring_Tutorial_Text.FCStd?raw=true Draft_Shapestring_Text] |
|Files=[https://github.com/FreeCAD/Examples/blob/master/Draft_Shapestring_Tutorial_Examples/Draft_Shapestring_Tutorial_Text.FCStd?raw=true Draft_Shapestring_Text] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
</div> |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==Introduzione== |
==Introduzione== |
||
In questo tutorial vedremo come |
In questo tutorial vedremo come |
||
| Line 15: | Line 18: | ||
* posizionarlo nello spazio 3D usando il [[placement/it|posizionamento]] e [[Draft Move/it|Draft Sposta]] con degli schizzi come elementi di supporto |
* posizionarlo nello spazio 3D usando il [[placement/it|posizionamento]] e [[Draft Move/it|Draft Sposta]] con degli schizzi come elementi di supporto |
||
* inciderlo mediante l'applicazione di un taglio booleano |
* inciderlo mediante l'applicazione di un taglio booleano |
||
</div> |
|||
This tutorial was originally written by Roland Frank (†2017, r-frank), and it was rewritten and re-illustrated by vocx. |
|||
This tutorial describes a method to create 3D text and use it with solid objects. We will discuss how to |
|||
* insert outlined text with the {{Button|[[Image:Draft_ShapeString.svg|16px]] [[Draft_ShapeString|Draft ShapeString]]}} tool, |
|||
* extrude it to be a 3D solid with {{Button|[[File:Part_Extrude.svg|16px]] [[Part Extrude|Part Extrude]]}}, |
|||
* position it in 3D space using [[placement|placement]], and {{Button|[[File:Draft_Move.svg|16px]] [[Draft Move|Draft Move]]}} (it uses a sketch as auxiliary geometry), and |
|||
* engrave the text by applying a boolean {{Button|[[File:Part_Cut.svg|16px]] [[Part Cut|Part Cut]]}}. |
|||
To use ShapeStrings inside the [[PartDesign Workbench|PartDesign Workbench]] go to the end of this tutorial. |
|||
[[File:08_T04_Part_ShapesString_Extrude_final_cut.png]] |
|||
{{Caption|Final model of the engraved text.}} |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
Si raccomanda di aver completato prima i tutorial di Sketcher. |
Si raccomanda di aver completato prima i tutorial di Sketcher. |
||
</div> |
|||
== Setup == |
|||
1. Open FreeCAD, create a new empty document with {{MenuCommand|File → [[File:Std_New.svg|16px]] [[Std_New|New]]}}, and switch to the [[Part Workbench|Part Workbench]]. |
|||
:1.1. Press the {{Button|[[File:Std_ViewIsometric.svg|16px]] [[Std_ViewIsometric|View isometric]]}} button, or press {{KEY|0}} in the numerical pad of your keyboard, to change the view to isometric to visualize the 3D solids better. |
|||
:1.2. Press the {{Button|[[File:Std_ViewFitAll.svg|16px]] [[Std_ViewFitAll|View fit all]]}} button whenever you add objects in order to pan and zoom the [[3D_view|3D view]] so that all elements are seen in the view. |
|||
:1.3. Hold {{KEY|Ctrl}} while you click to select multiple items. If you selected something wrong or want to de-select everything, just click on empty space in the [[3D view|3D view]]. |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==Creare la forma di base== |
==Creare la forma di base== |
||
*Avviare FreeCAD e creare un nuovo documento |
*Avviare FreeCAD e creare un nuovo documento |
||
| Line 30: | Line 57: | ||
*Assicurarsi che l'oggetto "Smusso" sia selezionato nella vista ad albero e premere <Spazio> per commutare la visibilità |
*Assicurarsi che l'oggetto "Smusso" sia selezionato nella vista ad albero e premere <Spazio> per commutare la visibilità |
||
[[Image:TutorialDraftShapeString_BasicShape.jpg|300px]] |
[[Image:TutorialDraftShapeString_BasicShape.jpg|300px]] |
||
</div> |
|||
2. Insert a primitive cube by clicking on {{Button|[[Image:Part_Box.svg|16px]] [[Part_Box|Box]]}}. |
|||
:2.1. Select {{incode|Cube}} in the [[tree view|tree view]]. |
|||
:2.2. Change the dimensions in the {{MenuCommand|Data}} tab of the [[property editor|property editor]]. |
|||
:2.3. Change {{MenuCommand|Width}} to {{incode|31 mm}}. |
|||
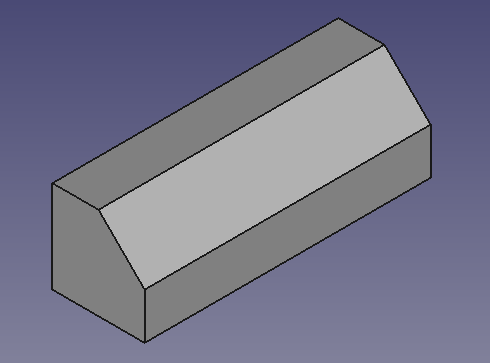
3. Create a chamfer. |
|||
:3.1. Select the upper edge ({{incode|Edge6}}) on the front face of the {{incode|Cube}} in the [[3D view|3D view]]. |
|||
:3.2. Press {{Button|[[Image:Part_Chamfer.svg|16px]] [[Part_Chamfer|Chamfer]]}}. |
|||
:3.3. In the {{MenuCommand|Chamfer edges}} [[task panel|task panel]] go to {{MenuCommand|Selection}}, choose {{MenuCommand|Select edges}}. As {{MenuCommand|Fillet type}} choose {{incode|Constant length}}, then set {{MenuCommand|Length}} to {{incode|5 mm}}. |
|||
:3.4. Press {{Button|OK}}. This will create a {{incode|Chamfer}} object. |
|||
:3.5. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|Chafmer}}, in the {{MenuCommand|View}} tab change the value of {{MenuCommand|Line Width}} to {{incode|2.0}}. |
|||
[[File:01_T04_Part_Cube_base_long.png]] |
|||
{{Caption|Base object created from a cube and a chamfer operation.}} |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==Inserire il testo con lo strumento ShapeString di Draft== |
==Inserire il testo con lo strumento ShapeString di Draft== |
||
*Passare all'ambiente Draft |
*Passare all'ambiente Draft |
||
| Line 47: | Line 91: | ||
**Ora fornire a FreeCAD il percorso al Font di testo "TTF" da usare (per esempio ARIAL-TTF) |
**Ora fornire a FreeCAD il percorso al Font di testo "TTF" da usare (per esempio ARIAL-TTF) |
||
**Dopo aver premuto {{KEY| Return}} un'ultima volta, nella struttura ad albero viene creato l'oggetto Forma da testo di Draft |
**Dopo aver premuto {{KEY| Return}} un'ultima volta, nella struttura ad albero viene creato l'oggetto Forma da testo di Draft |
||
</div> |
|||
4. Switch to the [[Draft Workbench|Draft Workbench]]. |
|||
:4.1. Make sure nothing is selected in the [[tree view|tree view]]. |
|||
:4.2. Establish the working plane to XY (Top) by clicking on {{Button|[[File:Draft_SelectPlane.svg|16px]] [[Draft_SelectPlane|SelectPlane]]}} and pressing {{Button|[[File:View-top.svg|16px]] [[Std_ViewTop|Top (XY)]]}}. |
|||
5. Insert the text "FreeCAD". |
|||
:5.1. Press on {{Button|[[File:Draft_ShapeString.svg|16px]] [[Draft_ShapeString|ShapeString]]}}. |
|||
:5.2. Change {{MenuCommand|X}} to {{incode|0 mm}}. |
|||
:5.3. Change {{MenuCommand|Y}} to {{incode|0 mm}}. |
|||
:5.4. Change {{MenuCommand|Z}} to {{incode|0 mm}}. |
|||
:5.5. Or press {{Button|Reset point}}. |
|||
:5.6. Change {{MenuCommand|String}} to {{incode|FreeCAD}}; change {{MenuCommand|Height}} to {{incode|5 mm}}; change {{MenuCommand|Tracking}} to {{incode|0 mm}}. |
|||
:5.7. Make sure {{MenuCommand|Font file}} points to a valid font, for example, {{incode|/usr/share/fonts/truetype/dejavu/DejaVuSans.ttf}}. Press the ellipsis {{Button|...}} to open the operating system's dialog to find a font. |
|||
:5.8. Press {{Button|OK}}. This will create a {{incode|ShapeString}} object. |
|||
:5.9. Recompute the document by pressing {{Button|[[File:Std_Refresh.svg|16px]] [[Std_Refresh|Refresh]]}}. |
|||
:5.10. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|ShapeString}}, in the {{MenuCommand|View}} tab change the value of {{MenuCommand|Line Width}} to {{incode|2.0}}. |
|||
:5.11. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|Chamfer}}, in the {{MenuCommand|View}} tab change the value of {{MenuCommand|Visibility}} to {{incode|false}}, or press {{KEY|Space}} in the keyboard. This will hide the object, so you can see the {{incode|ShapeString}} better. |
|||
:5.12. To see the ShapeString from above change the view by pressing {{Button|[[File:View-top.svg|16px]] [[Std_ViewTop|Top (XY)]]}}, or {{KEY|2}} in the keyboard. |
|||
:5.13. To restore the view to isometric, press {{Button|[[File:Std_ViewIsometric.svg|16px]] [[Std_ViewIsometric|View isometric]]}}, or {{KEY|0}} in the keyboard. |
|||
[[File:02_T04_Part_ShapeString.png]] |
|||
{{Caption|Text created as a ShapeString, that is, as a collection of edges in a plane.}} |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==Creare il testo 3D== |
==Creare il testo 3D== |
||
*Passare all'ambiente Part |
*Passare all'ambiente Part |
||
| Line 57: | Line 125: | ||
*Assicurarsi che l'oggetto "Estrusione" sia selezionato nella vista ad albero e premere <Spazio> per commutare la visibilità in visibile |
*Assicurarsi che l'oggetto "Estrusione" sia selezionato nella vista ad albero e premere <Spazio> per commutare la visibilità in visibile |
||
[[Image:TutorialDraftShapeString_DraftShapestring.jpg|300px]] |
[[Image:TutorialDraftShapeString_DraftShapestring.jpg|300px]] |
||
</div> |
|||
6. Switch back to the [[Part Workbench|Part Workbench]]. |
|||
:6.1. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|ShapeString}}, then press {{Button|[[File:Part_Extrude.svg|16px]] [[Part_Extrude|Extrude]]}}. |
|||
:6.2. In the {{MenuCommand|Extrude}} [[task panel|task panel]] go to {{MenuCommand|Direction}}, choose {{MenuCommand|Along normal}}; in {{MenuCommand|Length}}, set {{MenuCommand|Along}} to {{incode|1 mm}}; also tick the {{MenuCommand|Create solid}} option. |
|||
:6.3. Press {{Button|OK}}. This will create an {{incode|Extrude}} object. |
|||
:6.4. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|Extrude}}, in the {{MenuCommand|View}} tab change the value of {{MenuCommand|Line Width}} to {{incode|2.0}}. |
|||
[[File:03_T04_Part_ShapeString_Extrude.png]] |
|||
{{Caption|Text created as a ShapeString, and turned into a solid by extrusion.}} |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==Inserire lo schizzo per il posizionamento== |
==Inserire lo schizzo per il posizionamento== |
||
*Passare nell'ambiente Schizzo |
*Passare nell'ambiente Schizzo |
||
| Line 67: | Line 146: | ||
*Chiudere lo schizzo |
*Chiudere lo schizzo |
||
[[Image:TutorialDraftShapeString_Sketch.jpg|600px]] |
[[Image:TutorialDraftShapeString_Sketch.jpg|600px]] |
||
</div> |
|||
Now we will draw a simple sketch that will be used as auxiliary geometry to position the ShapeString extrusion. |
|||
7. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|Extrude}}, and press {{KEY|Space}} in the keyboard to make it invisible. |
|||
8. Switch to the [[Sketcher Workbench|Sketcher Workbench]]. |
|||
9. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|Chamfer}}, and press {{KEY|Space}} in the keyboard to make it visible. |
|||
:9.1. Choose the sloped face created by the chamfer operation ({{incode|Face3}}). |
|||
:9.2. Click on {{Button|[[File:Sketcher_NewSketch.svg|16px]] [[Sketcher_NewSketch|NewSketch]]}}. In the {{MenuCommand|Sketch attachment}} dialog, select {{incode|FlatFace}}, and press {{Button|OK}}. |
|||
:9.3. The view should adjust automatically so that the camera is parallel to the selected face. |
|||
:9.4. Draw a horizontal line in a general position on top of the face. The length is not important; we are just interested in its position. |
|||
:9.5. Constrain the left endpoint to be {{incode|2.5 mm}} away from the local X axis and from the local Y axis, using {{Button|[[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX.svg|16px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX|ConstrainDistanceX]]}} and {{Button|[[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceY.svg|16px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceY|ConstrainDistanceY]]}}. |
|||
:9.6. Since the sketch is just an auxiliary object, we don't need to have it fully constrained. You can do this if you wish by assigning a fixed distance, say, {{incode|20 mm}}, again with {{Button|[[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX.svg|16px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX|ConstrainDistanceX]]}}. |
|||
:9.7. Close the sketch. |
|||
[[File:04_T04_Part_ShapeString_support_sketch.png|500px]] |
|||
{{Caption|Line being created with the sketcher, with constraints.}} |
|||
[[File:05_T04_Part_ShapeString_support_sketch_3D.png|500px]] |
|||
{{Caption|Sketch line created on top of the solid face, to be used as reference guide for positioning the extruded text.}} |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==Posizionare il testo 3D nello spazio 3D== |
==Posizionare il testo 3D nello spazio 3D== |
||
*Assicurarsi che l'oggetto "Estrusione" sia selezionato nella vista ad albero e premere <Spazio> per commutare la visibilità in visibile |
*Assicurarsi che l'oggetto "Estrusione" sia selezionato nella vista ad albero e premere <Spazio> per commutare la visibilità in visibile |
||
| Line 80: | Line 182: | ||
*Nella vista 3D cliccare sul punto più alto dell'angolo sinistro dell'oggetto "Estrusione" (1) e quindi fare clic sul punto vincolato nello schizzo (2) |
*Nella vista 3D cliccare sul punto più alto dell'angolo sinistro dell'oggetto "Estrusione" (1) e quindi fare clic sul punto vincolato nello schizzo (2) |
||
[[Image:TutorialDraftShapeString_Position.jpg|600px]] |
[[Image:TutorialDraftShapeString_Position.jpg|600px]] |
||
</div> |
|||
10. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|Extrude}}, and press {{KEY|Space}} in the keyboard to make it visible. |
|||
11. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|Extrude}}, in the {{MenuCommand|Data}} tab of the [[property editor|property editor]], click on the {{MenuCommand|Placement}} value so the ellipsis button {{Button|...}} appears on the right. |
|||
:11.1. Tick the option {{MenuCommand|Apply incremental changes}}. |
|||
:11.2. Change the {{MenuCommand|Rotation}} to {{incode|Rotation axis with angle}}; {{MenuCommand|Axis}} to {{incode|Z}}, and {{MenuCommand|Angle}} to {{incode|90 deg}}, then click on {{Button|Apply}}. This will apply a rotation around the Z-axis, and will reset the {{MenuCommand|Angle}} field to zero. |
|||
:11.3. Change the {{MenuCommand|Rotation}} to {{incode|Rotation axis with angle}}; {{MenuCommand|Axis}} to {{incode|Y}}, and {{MenuCommand|Angle}} to {{incode|45 deg}}, then click on {{Button|Apply}}. This will apply a rotation around the Y-axis, and will reset the {{MenuCommand|Angle}} field to zero. |
|||
:11.4. Click on {{Button|OK}} to close the dialog. |
|||
12. Switch again to the [[Draft Workbench|Draft Workbench]]. |
|||
:12.1. Switch to "Wireframe" draw style with {{MenuCommand|View → [[Std_DrawStyle|Draw style]] → [[File:DrawStyleWireFrame.svg|16px]] Wireframe}}, or press the {{Button|[[File:DrawStyleWireFrame.svg|16px]] [[Std_DrawStyle|Wireframe]]}} button in the view toolbar. This will allow you to see the objects behind other objects. |
|||
:12.2. Make sure the [[Draft_Snap|Draft Snap]] "Snap to endpoint" method is active. This can be done from the menu {{MenuCommand|Draft → Snapping → [[File:Draft_ToggleSnap.svg|16px]] [[Draft_ToggleSnap|Toggle On/Off]]}}, and then {{MenuCommand| → [[File:Snap_Endpoint.svg|16px]] [[Draft Endpoint|Endpoint]]}}, or by pressing the {{Button|[[File:Draft_ToggleSnap.svg|16px]] [[Draft_ToggleSnap|ToggleSnap]]}} and {{Button|[[File:Snap_Endpoint.svg|16px]] [[Draft Endpoint|Snap endpoint]]}} buttons in the Snap toolbar. |
|||
13. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|Extrude}}. |
|||
:13.1. Click on {{Button|[[File:Draft_Move.svg|16px]] [[Draft Move|Move]]}}. |
|||
:13.2. In the [[3D view|3D view]] click on the upper left corner point of the {{incode|Extrude}} object (1), and then click on the leftmost point in the line drawn with the sketcher (2). |
|||
:13.3. If {{Button|[[File:Snap_Endpoint.svg|16px]] [[Draft Endpoint|Snap endpoint]]}} is active, as soon as you move the pointer close to a vertex, you should see that it attaches to it exactly. |
|||
:{{Emphasis|Note:}} if you have problems snapping to vertices, make sure only the {{Button|[[File:Snap_Endpoint.svg|16px]] [[Draft Endpoint|Snap endpoint]]}} method is enabled. Having multiple snapping methods active at the same time may make it difficult to select the right feature. |
|||
:13.4. The extruded text should now be inside the body of the {{incode|Fillet}} object. |
|||
[[File:06_T04_Part_ShapeString_move.svg]] |
|||
{{Caption|The extruded ShapeString should be moved to the position of the sketched line that lies on the face of the base body.}} |
|||
[[File:07_T04_Part_ShapesString_Extrude_in_place.png]] |
|||
{{Caption|Extruded ShapeString positioned in the {{incode|Fillet}}.}} |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==Creare il testo inciso== |
==Creare il testo inciso== |
||
*Passare all'ambiente Part |
*Passare all'ambiente Part |
||
| Line 92: | Line 221: | ||
*Finito |
*Finito |
||
[[Image:TutorialDraftShapeString_Complete.jpg|300px]] |
[[Image:TutorialDraftShapeString_Complete.jpg|300px]] |
||
</div> |
|||
14. Switch back to the [[Part Workbench|Part Workbench]]. |
|||
:14.1. Switch to "As is" draw style with {{MenuCommand|View → [[Std_DrawStyle|Draw style]] → [[File:DrawStyleAsIs.svg|16px]] As is}}, or press the {{Button|[[File:DrawStyleAsIs.svg|16px]] [[Std_DrawStyle|As is]]}} button in the view toolbar. This will show all objects with the normal shading and color. |
|||
:14.2. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|Sketch}}, and press {{KEY|Space}} in the keyboard to make it invisible. |
|||
15. In the [[tree view|tree view]] select {{incode|Chamfer}} first, and then {{incode|Extrude}}. |
|||
:15.1. Then press {{Button|[[File:Part_Cut.svg|16px]] [[Part_Cut|Cut]]}}. This will create a {{incode|Cut}} object. This is the final object. |
|||
:{{Emphasis|Note:}} the order in which you select the objects is important for the cut operation. The base object is selected first, and the subtracting object comes at the end. |
|||
:15.2. In the [[tree view|tree view]], select {{incode|Cut}}, in the {{MenuCommand|View}} tab change the value of {{MenuCommand|Line Width}} to {{incode|2.0}}. |
|||
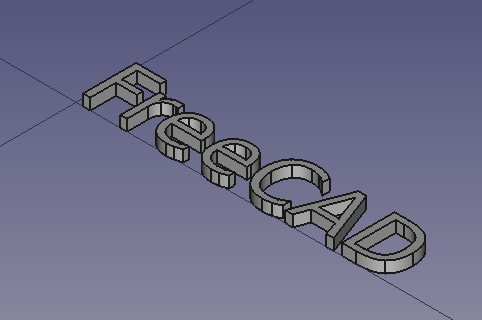
[[File:08_T04_Part_ShapesString_Extrude_final_cut.png]] |
|||
{{Caption|Final model of a filleted cube, with carved text created from a ShapeString, Extrude, and boolean Cut operations.}} |
|||
== Engraving 3D text with the PartDesign Workbench == |
|||
A similar process as described above can be done with the [[PartDesign_Workbench|PartDesign Workbench]]. |
|||
# Create the {{Button|[[File:Draft_ShapeString.svg|16px]] [[Draft_ShapeString|Draft ShapeString]]}} first. |
|||
# Create a {{Button|[[File:PartDesign_Body_Tree.svg|16px]] [[PartDesign_Body|PartDesign Body]]}}, make it active, and add a base solid by adding primitives, or using a Sketch and extruding it with {{Button|[[File:PartDesign_Pad.svg|16px]] [[PartDesign_Pad|PartDesign Pad]]}}. |
|||
# Move the {{incode|ShapeString}} object into the active body. |
|||
# Attach the {{incode|ShapeString}} object to one of the faces of the solid, or to a {{Button|[[File:PartDesign_Plane.svg|16px]] [[PartDesign Plane|PartDesign Plane]]}}, using {{Button|[[File:Part_Attachment.svg|16px]] [[Part_Attachment|Part Attachment]]}}. |
|||
# Now create a {{Button|[[File:PartDesign_Pad.svg|16px]] [[PartDesign_Pad|PartDesign Pad]]}} or a {{Button|[[File:PartDesign_Pocket.svg|16px]] [[PartDesign_Pocket|PartDesign Pocket]]}} from the {{incode|ShapeString}}, in order to produce an additive or a subtractive feature of the base body, respectively. |
|||
See the forum thread, [https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=36623 How to use ShapeStrings in PartDesign]. |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==Note== |
==Note== |
||
*Per creare un testo curvo è possibile utilizzare la macro [[Macro_Circular Text/it|Testo circolare]][[File:FCCircularTextButtom.png|32px]] |
*Per creare un testo curvo è possibile utilizzare la macro [[Macro_Circular Text/it|Testo circolare]][[File:FCCircularTextButtom.png|32px]] |
||
| Line 98: | Line 253: | ||
*L'estrusione della Forma stringa di testo può essere fatta anche con lo strumento Pad di PartDesign |
*L'estrusione della Forma stringa di testo può essere fatta anche con lo strumento Pad di PartDesign |
||
*Ricordare che l'oggetto DraftShapestring non può essere mappato su una faccia (quindi non è possibile nessun comando Tasca ) |
*Ricordare che l'oggetto DraftShapestring non può essere mappato su una faccia (quindi non è possibile nessun comando Tasca ) |
||
</div> |
|||
* To create curved text you can use the macro [[File:FCCircularTextButtom.png|32px]] [[Macro_Circular_Text|Circular Text]]. |
|||
* To import text from an SVG file look at the [[Import_text_and_geometry_from_Inkscape|Import text and geometry from Inkscape]] tutorial. |
|||
{{Userdocnavi}} |
|||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
Revision as of 15:39, 24 November 2019
| Argomento |
|---|
| Forma da Testo (Draft) |
| Livello di difficoltà |
| Base |
| Tempo di esecuzione |
| 30 minuti |
| Autori |
| r-frank |
| Versione di FreeCAD |
| 0.16.6704 |
| Files di esempio |
| Draft_Shapestring_Text |
| Vedere anche |
| Nessuno |
Introduzione
In questo tutorial vedremo come
- inserire un testo con lo strumento
 Forma da testo (ShapeString)
Forma da testo (ShapeString) - estruderlo per creare un solido
- posizionarlo nello spazio 3D usando il posizionamento e Draft Sposta con degli schizzi come elementi di supporto
- inciderlo mediante l'applicazione di un taglio booleano
This tutorial was originally written by Roland Frank (†2017, r-frank), and it was rewritten and re-illustrated by vocx.
This tutorial describes a method to create 3D text and use it with solid objects. We will discuss how to
- insert outlined text with the
Draft ShapeString tool,
- extrude it to be a 3D solid with
Part Extrude,
- position it in 3D space using placement, and
Draft Move (it uses a sketch as auxiliary geometry), and
- engrave the text by applying a boolean
Part Cut.
To use ShapeStrings inside the PartDesign Workbench go to the end of this tutorial.
Final model of the engraved text.
Si raccomanda di aver completato prima i tutorial di Sketcher.
Setup
1. Open FreeCAD, create a new empty document with File → New, and switch to the Part Workbench.
- 1.1. Press the
View isometric button, or press 0 in the numerical pad of your keyboard, to change the view to isometric to visualize the 3D solids better.
- 1.2. Press the
View fit all button whenever you add objects in order to pan and zoom the 3D view so that all elements are seen in the view.
- 1.3. Hold Ctrl while you click to select multiple items. If you selected something wrong or want to de-select everything, just click on empty space in the 3D view.
Creare la forma di base
- Avviare FreeCAD e creare un nuovo documento
- Passare all'ambiente Part
- Inserire un cubo cliccando su

- Assicurarsi che il cubo sia selezionato nella vista ad albero
- Modificare la larghezza fino a 31 mm utilizzando la scheda dati nella finestra delle proprietà
- Cliccare su
per passare alla vista isometrica
- Cliccare su File:View-zoom-all.svg per adattare la vista a tutto l'oggetto
- Nella vista 3D selezionare il bordo superiore sulla faccia anteriore del cubo
- Applicare uno smusso (a Edge6) di 5 mm cliccando su

- Assicurarsi che l'oggetto "Smusso" sia selezionato nella vista ad albero e premere <Spazio> per commutare la visibilità
2. Insert a primitive cube by clicking on Box.
- 2.1. Select
Cubein the tree view. - 2.2. Change the dimensions in the Data tab of the property editor.
- 2.3. Change Width to
31 mm.
3. Create a chamfer.
- 3.1. Select the upper edge (
Edge6) on the front face of theCubein the 3D view. - 3.2. Press
Chamfer.
- 3.3. In the Chamfer edges task panel go to Selection, choose Select edges. As Fillet type choose
Constant length, then set Length to5 mm. - 3.4. Press OK. This will create a
Chamferobject. - 3.5. In the tree view, select
Chafmer, in the View tab change the value of Line Width to2.0.
Base object created from a cube and a chamfer operation.
Inserire il testo con lo strumento ShapeString di Draft
- Passare all'ambiente Draft
- Assicurarsi che nella vista ad albero non sia selezionato nulla
- Passare al piano di lavoro XY (dall'alto) cliccando su
 Auto e sceglindo XY
Auto e sceglindo XY - Inserire il testo "FreeCAD" in questo modo
- Cliccare su

- Evidenziare il testo nel campo "Global X" e digitare "0" sulla tastiera, poi premere Return
- Evidenziare il testo nel campo "Global Y"
- Digitare "0" sulla tastiera, poi premere Return
- Evidenziare il testo nel campo "Global Z"
- Digitare "0" sulla tastiera, poi premere Return
- Digitare "FreeCAD" nel campo della stringa (senza parentesi) e premere Return
- Scegliere una altezza di 5mm
- Scegliere un tracking di 0 mm
- Ora fornire a FreeCAD il percorso al Font di testo "TTF" da usare (per esempio ARIAL-TTF)
- Dopo aver premuto Return un'ultima volta, nella struttura ad albero viene creato l'oggetto Forma da testo di Draft
- Cliccare su
4. Switch to the Draft Workbench.
- 4.1. Make sure nothing is selected in the tree view.
- 4.2. Establish the working plane to XY (Top) by clicking on
SelectPlane and pressing
Top (XY).
5. Insert the text "FreeCAD".
- 5.1. Press on
ShapeString.
- 5.2. Change X to
0 mm. - 5.3. Change Y to
0 mm. - 5.4. Change Z to
0 mm. - 5.5. Or press Reset point.
- 5.6. Change String to
FreeCAD; change Height to5 mm; change Tracking to0 mm. - 5.7. Make sure Font file points to a valid font, for example,
/usr/share/fonts/truetype/dejavu/DejaVuSans.ttf. Press the ellipsis ... to open the operating system's dialog to find a font. - 5.8. Press OK. This will create a
ShapeStringobject. - 5.9. Recompute the document by pressing
Refresh.
- 5.10. In the tree view, select
ShapeString, in the View tab change the value of Line Width to2.0. - 5.11. In the tree view, select
Chamfer, in the View tab change the value of Visibility tofalse, or press Space in the keyboard. This will hide the object, so you can see theShapeStringbetter. - 5.12. To see the ShapeString from above change the view by pressing
Top (XY), or 2 in the keyboard.
- 5.13. To restore the view to isometric, press
View isometric, or 0 in the keyboard.
Text created as a ShapeString, that is, as a collection of edges in a plane.
Creare il testo 3D
- Passare all'ambiente Part
- Assicurarsi che nella struttura ad albero l'oggetto Shapestring sia selezionato
- Usare lo strumento Estrusione di Part
 con i parametri:
con i parametri:
- estrusione Z=1 mm
- assicurarsi di spuntare "Crea solido"
- usare "OK" per terminare l'estrusione delle parti
- Assicurarsi che l'oggetto "Estrusione" sia selezionato nella vista ad albero e premere <Spazio> per commutare la visibilità in visibile
6. Switch back to the Part Workbench.
- 6.1. In the tree view, select
ShapeString, then pressExtrude.
- 6.2. In the Extrude task panel go to Direction, choose Along normal; in Length, set Along to
1 mm; also tick the Create solid option. - 6.3. Press OK. This will create an
Extrudeobject. - 6.4. In the tree view, select
Extrude, in the View tab change the value of Line Width to2.0.
Text created as a ShapeString, and turned into a solid by extrusion.
Inserire lo schizzo per il posizionamento
- Passare nell'ambiente Schizzo
- Assicurarsi che l'oggetto "Smusso" sia selezionato nella vista ad albero e premere <Spazio> per commutare la visibilità in visibile
- Scegliere la faccia inclinata creata dall'operazione smusso
- Cliccare su
 per inserire un nuovo schizzo
per inserire un nuovo schizzo - Disegnare una linea (può essere orizzontale o verticale, la lunghezza non è importante ...)
- Vincolare uno dei punti finali a +2,5 mm di distanza verticale e +2,5 mm di distanza orizzontale dall'origine
- Chiudere lo schizzo
Now we will draw a simple sketch that will be used as auxiliary geometry to position the ShapeString extrusion.
7. In the tree view, select Extrude, and press Space in the keyboard to make it invisible.
8. Switch to the Sketcher Workbench.
9. In the tree view, select Chamfer, and press Space in the keyboard to make it visible.
- 9.1. Choose the sloped face created by the chamfer operation (
Face3). - 9.2. Click on
NewSketch. In the Sketch attachment dialog, select
FlatFace, and press OK. - 9.3. The view should adjust automatically so that the camera is parallel to the selected face.
- 9.4. Draw a horizontal line in a general position on top of the face. The length is not important; we are just interested in its position.
- 9.5. Constrain the left endpoint to be
2.5 mmaway from the local X axis and from the local Y axis, usingConstrainDistanceX and
ConstrainDistanceY.
- 9.6. Since the sketch is just an auxiliary object, we don't need to have it fully constrained. You can do this if you wish by assigning a fixed distance, say,
20 mm, again withConstrainDistanceX.
- 9.7. Close the sketch.
Line being created with the sketcher, with constraints.
Sketch line created on top of the solid face, to be used as reference guide for positioning the extruded text.
Posizionare il testo 3D nello spazio 3D
- Assicurarsi che l'oggetto "Estrusione" sia selezionato nella vista ad albero e premere <Spazio> per commutare la visibilità in visibile
- Assicurarsi che nella vista ad albero sia selezionato l'oggetto "Estrusione"
- Applicare un posizionamento incrementale, asse di rotazione Z=90°
- Applicare un posizionamento incrementale, asse di rotazione Y=45°
- Passare nell'ambiente Draft
- Passare alla modalità di vista Wireframe
- Assicurarsi che sia attivo solo l'aggancio a un "Punto finale" Draft->Snap->Snap a un punto finale
- Selezionare l'oggetto "Estrusione"
- Cliccare su

- Nella vista 3D cliccare sul punto più alto dell'angolo sinistro dell'oggetto "Estrusione" (1) e quindi fare clic sul punto vincolato nello schizzo (2)
10. In the tree view, select Extrude, and press Space in the keyboard to make it visible.
11. In the tree view, select Extrude, in the Data tab of the property editor, click on the Placement value so the ellipsis button ... appears on the right.
- 11.1. Tick the option Apply incremental changes.
- 11.2. Change the Rotation to
Rotation axis with angle; Axis toZ, and Angle to90 deg, then click on Apply. This will apply a rotation around the Z-axis, and will reset the Angle field to zero. - 11.3. Change the Rotation to
Rotation axis with angle; Axis toY, and Angle to45 deg, then click on Apply. This will apply a rotation around the Y-axis, and will reset the Angle field to zero. - 11.4. Click on OK to close the dialog.
12. Switch again to the Draft Workbench.
- 12.1. Switch to "Wireframe" draw style with View → Draw style →
Wireframe, or press the
Wireframe button in the view toolbar. This will allow you to see the objects behind other objects.
- 12.2. Make sure the Draft Snap "Snap to endpoint" method is active. This can be done from the menu Draft → Snapping → File:Draft ToggleSnap.svg Toggle On/Off, and then → File:Snap Endpoint.svg Endpoint, or by pressing the File:Draft ToggleSnap.svg ToggleSnap and File:Snap Endpoint.svg Snap endpoint buttons in the Snap toolbar.
13. In the tree view, select Extrude.
- 13.1. Click on
Move.
- 13.2. In the 3D view click on the upper left corner point of the
Extrudeobject (1), and then click on the leftmost point in the line drawn with the sketcher (2). - 13.3. If File:Snap Endpoint.svg Snap endpoint is active, as soon as you move the pointer close to a vertex, you should see that it attaches to it exactly.
- Note: if you have problems snapping to vertices, make sure only the File:Snap Endpoint.svg Snap endpoint method is enabled. Having multiple snapping methods active at the same time may make it difficult to select the right feature.
- 13.4. The extruded text should now be inside the body of the
Filletobject.
The extruded ShapeString should be moved to the position of the sketched line that lies on the face of the base body.
Extruded ShapeString positioned in the Fillet.
Creare il testo inciso
- Passare all'ambiente Part
- Passare alla modalità di vista "Come è"
- Nella vista ad albero selezionare il testo 3D ("estrusione") e poi l'oggetto di base ("smusso")
- Applicare un taglio booleano cliccando su

- Assicurarsi che nella vista ad albero sia selezionato l'oggetto "Sketch"
- Premere <Spazio> per commutare la visibilità
- Cliccare su
per passare alla vista isometrica
- Cliccare su File:View-zoom-all.svg per adattare la vista all'oggetto
- Finito
14. Switch back to the Part Workbench.
- 14.1. Switch to "As is" draw style with View → Draw style →
As is, or press the
As is button in the view toolbar. This will show all objects with the normal shading and color.
- 14.2. In the tree view, select
Sketch, and press Space in the keyboard to make it invisible.
15. In the tree view select Chamfer first, and then Extrude.
- 15.1. Then press
Cut. This will create a
Cutobject. This is the final object. - Note: the order in which you select the objects is important for the cut operation. The base object is selected first, and the subtracting object comes at the end.
- 15.2. In the tree view, select
Cut, in the View tab change the value of Line Width to2.0.
Final model of a filleted cube, with carved text created from a ShapeString, Extrude, and boolean Cut operations.
Engraving 3D text with the PartDesign Workbench
A similar process as described above can be done with the PartDesign Workbench.
- Create the
Draft ShapeString first.
- Create a
PartDesign Body, make it active, and add a base solid by adding primitives, or using a Sketch and extruding it with
PartDesign Pad.
- Move the
ShapeStringobject into the active body. - Attach the
ShapeStringobject to one of the faces of the solid, or to aPartDesign Plane, using
Part Attachment.
- Now create a
PartDesign Pad or a
PartDesign Pocket from the
ShapeString, in order to produce an additive or a subtractive feature of the base body, respectively.
See the forum thread, How to use ShapeStrings in PartDesign.
Note
- Per creare un testo curvo è possibile utilizzare la macro Testo circolare

- Per importare un testo da Inkscape vedere il tutorial Importare testo e geometria da Inkscape
- L'estrusione della Forma stringa di testo può essere fatta anche con lo strumento Pad di PartDesign
- Ricordare che l'oggetto DraftShapestring non può essere mappato su una faccia (quindi non è possibile nessun comando Tasca )
- To create curved text you can use the macro
 Circular Text.
Circular Text. - To import text from an SVG file look at the Import text and geometry from Inkscape tutorial.
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Start, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework, Web
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub