Îndrumător de modelare 3D a fonturilor cu ShapeString
| Topic |
|---|
| ShapeString (Draft workbench) |
| Level |
| Beginner |
| Time to complete |
| 30 minutes |
| Authors |
| r-frank |
| FreeCAD version |
| 0.16.6704 |
| Example files |
| Draft_Shapestring_Text |
| See also |
| None |
Introducere
În această lecţie vom discuta:
- insert a text with the
 ShapeString tool
ShapeString tool - extrude it to be a solid
- position it in 3D space using placement and Draft Move with sketches as helper elements
- doing an engraving by applying a boolean cut
This tutorial was originally written by Roland Frank (†2017, r-frank), and it was rewritten and re-illustrated by vocx.
This tutorial describes a method to create 3D text and use it with solid objects in the Part Workbench. We will discuss how to
- insert outlined text with the
Draft ShapeString tool,
- extrude it to be a 3D solid with
Part Extrude,
- position it in 3D space using placement, and
Draft Move (it uses a sketch as auxiliary geometry), and
- engrave the text by applying a boolean
Part Cut.
To use ShapeStrings inside the PartDesign Workbench, the process is essentially the same as with the Part Workbench, but the ShapeString is placed inside the PartDesign Body to extrude it. Go to the end of this tutorial for more information.
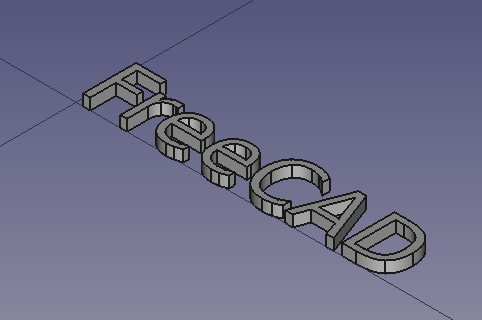
Final model of the engraved text.
Se recomandă să fi terminat mai întâi tutorialul sketcher.
Setup
1. Open FreeCAD, create a new empty document with File → New, and switch to the Part Workbench.
- 1.1. Press the
View isometric button, or press 0 in the numerical pad of your keyboard, to change the view to isometric to visualize the 3D solids better.
- 1.2. Press the
View fit all button whenever you add objects in order to pan and zoom the 3D view so that all elements are seen in the view.
- 1.3. Hold Ctrl while you click to select multiple items. If you selected something wrong or want to de-select everything, just click on empty space in the 3D view.
Crearea de forme de bază
- Start FreeCAD și creați un nou document
- Comutați la Atelierul Part/Piese
- Inserați un cub făcând click pe

- Make sure the cube is selected in the tree view
- Change width to be 31 mm by using the data-tab in the property view
- Click on
 to change to axometric view
to change to axometric view - Click on
 to zoom to fit all
to zoom to fit all - Select upper edge on the front face of the cube in 3D view
- Apply a chamfer (to Edge6) of 5 mm by clicking on

- Make sure object "chamfer" is selected in the tree view and press <Space> to toggle visibility
2. Insert a primitive cube by clicking on Box.
- 2.1. Select
Cubein the tree view. - 2.2. Change the dimensions in the Data tab of the property editor.
- 2.3. Change Width to
31 mm.
3. Create a chamfer.
- 3.1. Select the upper edge (
Edge6) on the front face of theCubein the 3D view. - 3.2. Press
Chamfer.
- 3.3. In the Chamfer edges task panel go to Selection, choose Select edges. As Chamfer type choose
Equal distance, then set Length to5 mm. - 3.4. Press OK. This will create a
Chamferobject. - 3.5. In the tree view, select
Chamfer, in the View tab change the value of Line Width to2.0.
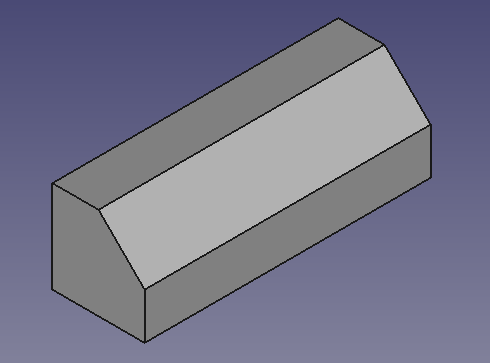
Base object created from a cube and a chamfer operation.
Inserarea de text cu instrumentul Draft ShapeString
- Switch to Draft workbench
- make sure nothing is selected in the tree view
- Toggle working plane to XY (Top) by clicking on
 Auto and choosing XY
Auto and choosing XY - Insert text "FreeCAD" by
- Click on

- Highlight the text in the "Global X"-field and type "0" on the keyboard and press Return
- Highlight the text in the "Global Y" field
- Type "0" on the keyboard and press Return
- Highlight the text in the "Global Z" field
- Type "0" on the keyboard and press Return
- Enter "FreeCAD" in the string field (without brackets) and press Return
- Choose a height of 5mm
- Choose a tracking of 0 mm
- now point FreeCAD to a "TTF"-Text-Font to use (for example the ARIAL-TTF)
- After pressing Return one last time, the Draft-Shapestring object is created in the tree view
- Click on
4. Switch to the Draft Workbench.
- 4.1. Make sure nothing is selected in the tree view.
- 4.2. Establish the working plane to XY (Top) by clicking on
SelectPlane and pressing
Top (XY).
5. Insert the text "FreeCAD".
- 5.1. Click on
ShapeString.
- 5.2. Change X to
0 mm. - 5.3. Change Y to
0 mm. - 5.4. Change Z to
0 mm. - 5.5. Or press Reset point.
- 5.6. Change String to
FreeCAD; change Height to5 mm; change Tracking to0 mm. - 5.7. Make sure Font file points to a valid font, for example,
/usr/share/fonts/truetype/dejavu/DejaVuSans.ttf. Press the ellipsis ... to open the operating system's dialog to find a font.- Note: for more details about working with fonts please refer to the Draft ShapeString Notes section.
- 5.8. Press OK. This will create a
ShapeStringobject. - 5.9. Recompute the document by pressing
Refresh.
- 5.10. In the tree view, select
ShapeString, in the View tab change the value of Line Width to2.0. - 5.11. In the tree view, select
Chamfer, in the View tab change the value of Visibility tofalse, or press Space in the keyboard. This will hide the object, so you can see theShapeStringbetter. - 5.12. To see the ShapeString from above change the view by pressing
Top (XY), or 2 in the keyboard.
- 5.13. To restore the view to isometric, press
View isometric, or 0 in the keyboard.
Text created as a ShapeString, that is, as a collection of edges in a plane.
Crearea de texte 3D
- Comutați pe Atelierul de Piese(Part workbench)
- Make sure the object "Shapestring" is selected in the tree view
- Use Part Extrude-Tool
 with the parameters:
with the parameters:
- extrude Z=1 mm
- make sure to tick "create solid"
- use "OK" to finish part extrude operation
- Make sure object "Extrude" is selected in the tree view and press <Space> to toggle its visibility to be visible
6. Switch back to the Part Workbench.
- 6.1. In the tree view, select
ShapeString, then pressExtrude.
- 6.2. In the Extrude task panel go to Direction, choose Along normal; in Length, set Along to
1 mm; also tick the Create solid option. - 6.3. Press OK. This will create an
Extrudeobject. - 6.4. In the tree view, select
Extrude, in the View tab change the value of Line Width to2.0.
Text created as a ShapeString, and turned into a solid by extrusion.
Inserarea schiței pentru poziționare
- Switch to sketcher workbench
- Make sure object "chamfer" is selected in the tree view and press <Space> to toggle its visibility to visible
- Choose sloped face created by chamfer operation
- Click on
 to insert new sketch
to insert new sketch - Draw a line (may be horizontal or vertical, length is not of importance ...)
- Constrain one of the endpoints to be +2,5 mm vertical distance and +2,5 mm horizontal distance away from the origin
- Close the sketch
Now we will draw a simple sketch that will be used as auxiliary geometry to position the ShapeString extrusion.
7. In the tree view, select Extrude, and press Space in the keyboard to make it invisible.
8. Switch to the Sketcher Workbench.
9. In the tree view, select Chamfer, and press Space in the keyboard to make it visible.
- 9.1. Choose the sloped face created by the chamfer operation (
Face3). - 9.2. Click on
NewSketch. In the Sketch attachment dialog, select
FlatFace, and press OK. - 9.3. The view should adjust automatically so that the camera is parallel to the selected face.
- 9.4. Draw a horizontal line in a general position on top of the face. The length is not important; we are just interested in its position.
- 9.5. Constrain the left endpoint to be
2.5 mmaway from the local X axis and from the local Y axis, usingConstrainDistanceX and
ConstrainDistanceY.
- 9.6. Since the sketch is just an auxiliary object, we don't need to have it fully constrained. You can do this if you wish by assigning a fixed distance, say,
20 mm, again withConstrainDistanceX.
- 9.7. Close the sketch.
Line being created with the sketcher, with constraints.
Sketch line created on top of the solid face, to be used as reference guide for positioning the extruded text.
Posiționare text 3D în spațiul 3D
- Make sure object "Extrude" is selected in the tree view and press <Space> to toggle visibility to visible
- Make sure, object "Extrude" is selected in the tree view
- Open Placement task Edit->Placement...
- Apply incremental placement, axis of rotation Z=90°
- Apply incremental placement, axis of rotation Y=45°
- Switch to draft workbench
- Switch to wireframe mode
- Make sure, only "snap to endpoint" is activated Draft->Snapping->Snap to endpoint
- Select "extrude"-object
- Click on

- In 3D view click on the most upper left corner point of "extrude"-object (1) and then click on the constrained point in the sketch (2)
10. In the tree view, select Extrude, and press Space in the keyboard to make it visible.
11. With Extrude still selected, in the Data tab of the property editor, click on the Placement value so the ellipsis button ... appears on the right and click on that button.
- 11.1. Tick the option Apply incremental changes.
- 11.2. Change the Rotation to
Rotation axis with angle; Axis toZ(by setting theX,YandZvalues of the axis inputboxes to0,0and1respectively,Zis the third inputbox), and Angle to90 deg, then click on Apply. This will apply a rotation around the Z-axis, and will reset the Angle field to zero. - 11.3. Change the Rotation to
Rotation axis with angle; Axis toY(by setting theX,YandZvalues of the axis inputboxes to0,1and0respectively), and Angle to45 deg, then click on Apply. This will apply a rotation around the Y-axis, and will reset the Angle field to zero. - 11.4. Click on OK to close the dialog.
12. Switch again to the Draft Workbench.
- 12.1. Switch to "Wireframe" draw style with View → Draw style →
Wireframe, or press the
Wireframe button in the view toolbar. This will allow you to see the objects behind other objects.
- 12.2. Make sure the Draft Snap "Snap to endpoint" method is active. This can be done from the menu Draft → Snapping →
Toggle On/Off, and then →
Endpoint, or by pressing the
ToggleSnap and
Snap endpoint buttons in the Snap toolbar.
13. In the tree view, select Extrude.
- 13.1. Click on
Move.
- 13.2. In the 3D view click on the upper left corner point of the
Extrudeobject (1), and then click on the leftmost point in the line drawn with the sketcher (2). - 13.3. If
Snap endpoint is active, as soon as you move the pointer close to a vertex, you should see that it attaches to it exactly.
- Note: if you have problems snapping to vertices, make sure only the
Snap endpoint method is enabled. Having multiple snapping methods active at the same time may make it difficult to select the right feature.
- 13.4. The extruded text should now be inside the body of the
Chamferobject.
The extruded ShapeString should be moved to the position of the sketched line that lies on the face of the base body.
Extruded ShapeString positioned in the Chamfer.
Creaţi un text gravat
- Switch to part workbench
- Switch to "As is"-view mode
- Select the 3D text ("extrude") and then the base object ("chamfer") in the tree view
- Apply a boolean cut by clicking on

- Make sure object "Sketch" is selected in the tree view
- Press <Space> to toggle visibilty
- Click on
 to change to axometric view
to change to axometric view - Click on
 to zoom to fit all
to zoom to fit all - Finished
14. Switch back to the Part Workbench.
- 14.1. Switch to "As is" draw style with View → Draw style →
As is, or press the
As is button in the view toolbar. This will show all objects with the normal shading and color.
- 14.2. In the tree view, select
Sketch, and press Space in the keyboard to make it invisible.
15. In the tree view select Chamfer first, and then Extrude.
- 15.1. Then press
Cut. This will create a
Cutobject. This is the final object. - Note: the order in which you select the objects is important for the cut operation. The base object is selected first, and the subtracting object comes at the end.
- 15.2. In the tree view, select
Cut, in the View tab change the value of Line Width to2.0.
Final model of a filleted cube, with carved text created from a ShapeString, Extrude, and boolean Cut operations.
Engraving 3D text with the PartDesign Workbench
A similar process as described above can be done with the PartDesign Workbench.
- Create the
Draft ShapeString first.
- Create a
PartDesign Body, make it active, and add a base solid by adding primitives, or using a Sketch and extruding it with
PartDesign Pad.
- Move the
ShapeStringobject into the active body. - Attach the
ShapeStringobject to one of the faces of the solid, or to aPartDesign Plane, using
Part EditAttachment.
- Now create a
PartDesign Pad or a
PartDesign Pocket from the
ShapeString, in order to produce an additive or a subtractive feature of the base body, respectively.
See the forum thread, How to use ShapeStrings in PartDesign.
Notă
- To create curved text you can use
 Macro FCCircularText.
Macro FCCircularText. - To import text from an SVG file look at the Import text and geometry from Inkscape tutorial.
- Primitives: Box, Cylinder, Sphere, Cone, Torus, Tube, Create primitives, Shape builder
- Creation and modification: Extrude, Revolve, Mirror, Fillet, Chamfer, Make face from wires, Ruled Surface, Loft, Sweep, Section, Cross sections, 3D Offset, 2D Offset, Thickness, Projection on surface, Attachment
- Boolean: Make compound, Explode Compound, Compound Filter, Boolean, Cut, Fuse, Common, Connect, Embed, Cutout, Boolean fragments, Slice apart, Slice, XOR
- Measure: Measure Linear, Measure Angular, Measure Refresh, Clear All, Toggle All, Toggle 3D, Toggle Delta
- Structure tools: Part, Group
- Helper tools: Create body, Create sketch, Edit sketch, Map sketch to face
- Modeling tools
- Datum tools: Create a datum point, Create a datum line, Create a datum plane, Create a local coordinate system, Create a shape binder, Create a sub-object(s) shape binder, Create a clone
- Additive tools: Pad, Revolution, Additive loft, Additive pipe, Additive helix, Additive box, Additive cylinder, Additive sphere, Additive cone, Additive ellipsoid, Additive torus, Additive prism, Additive wedge
- Subtractive tools: Pocket, Hole, Groove, Subtractive loft, Subtractive pipe, Subtractive helix, Subtractive box, Subtractive cylinder, Subtractive sphere, Subtractive cone, Subtractive ellipsoid, Subtractive torus, Subtractive prism, Subtractive wedge
- Transformation tools: Mirrored, Linear Pattern, Polar Pattern, Create MultiTransform, Scaled
- Dress-up tools: Fillet, Chamfer, Draft, Thickness
- Boolean: Boolean operation
- Extras: Migrate, Sprocket, Involute gear, Shaft design wizard
- Context menu: Set tip, Move object to other body, Move object after other object, Appearance, Color per face
- General: Create sketch, Edit sketch, Map sketch to face, Reorient sketch, Validate sketch, Merge sketches, Mirror sketch, Leave sketch, View sketch, View section, Toggle grid, Toggle snap, Configure rendering order, Stop operation
- Sketcher geometries: Point, Line, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Circle, Circle by 3 points, Ellipse, Ellipse by 3 points, Arc of ellipse, Arc of hyperbola, Arc of parabola, B-spline by control points, Periodic B-spline by control points, B-spline by knots, Periodic B-spline by knots, Polyline, Rectangle, Centered rectangle, Rounded rectangle, Triangle, Square, Pentagon, Hexagon, Heptagon, Octagon, Regular polygon, Slot, Fillet, Corner-preserving fillet, Trim, Extend, Split, External geometry, Carbon copy, Toggle construction geometry
- Sketcher constraints:
- Geometric constraints: Coincident, Point on object, Vertical, Horizontal, Parallel, Perpendicular, Tangent, Equal, Symmetric, Block
- Dimensional constraints: Lock, Horizontal distance, Vertical distance, Distance, Radius or weight, Diameter, Auto radius/diameter, Angle, Refraction (Snell's law)
- Constraint tools: Toggle driving/reference constraint, Activate/deactivate constraint
- Sketcher tools: Select unconstrained DoF, Select associated constraints, Select associated geometry, Select redundant constraints, Select conflicting constraints, Show/hide internal geometry, Select origin, Select horizontal axis, Select vertical axis, Symmetry, Clone, Copy, Move, Rectangular array, Remove axes alignment, Delete all geometry, Delete all constraints
- Sketcher B-spline tools: Show/hide B-spline degree, Show/hide B-spline control polygon, Show/hide B-spline curvature comb, Show/hide B-spline knot multiplicity, Show/hide B-spline control point weight, Convert geometry to B-spline, Increase B-spline degree, Decrease B-spline degree, Increase knot multiplicity, Decrease knot multiplicity, Insert knot, Join curves
- Sketcher virtual space: Switch virtual space
- Additional: Sketcher Dialog, Preferences, Sketcher scripting
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Start, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework, Web
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub